Once driven by melodramatic drops successful early-life mortality, life expectancy gains are now losing momentum, signaling that today’s generations whitethorn ne'er lucifer nan near-linear longevity climb of nan past.

Study: Cohort mortality forecasts bespeak signs of deceleration successful life expectancy gains. Image Credit: Hyejin Kang / Shutterstock
In a caller study published successful nan journal Proceedings of nan National Academy of Sciences, researchers from nan Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research, INED, and nan University of Wisconsin-Madison estimated cohort life expectancy for commencement cohorts from 1939 to 2000 crossed 23 high-income countries, utilizing aggregate forecasting methods, and assessed whether gains are decelerating.
Background
Every twelvemonth of other life shapes budgets, pensions, and family plans, yet caller headlines pass that advancement whitethorn beryllium slowing. For a century, high-income countries saw near-linear gains arsenic vaccines, sanitation, and cardiac attraction reduced early and midlife deaths.
Period life expectancy summarizes mortality successful a almanac year, but cohort life expectancy tracks existent commencement cohorts and amended reflects lived longevity. Longevity besides depends connected economical stability, behavior, inequality, and emerging risks, including pandemics and nationalist wellness crises.
Policy and readying hinge connected knowing whether longevity gains are compounding, flattening, aliases shifting by age; further investigation is essential.
About nan study
The study utilized age-specific decease rates from nan Human Mortality Database (HMD) for 23 high-income, low-mortality countries. Birth cohorts from 1939 to 2000 were included astatine property 20 and above, to guarantee important observation.
Cohort mortality was forecasted to property 100+ for accuracy, and life tables were past closed astatine 85+. Two modeling strategies were applied. Period-based forecasts approximated cohort mortality by extracting nan Lexis diagonal and included Lee-Carter (LC), Smooth Constrained Mortality Forecasting CP-Splines (CPS), Compositional Data Analysis (CoDa), and nan United Nations World Population Prospects 2024 (UN WPP 2024) mean scenario. Cohort-specific models straight captured cohort trends utilizing nan Linear Lee-Carter (LLC) and Cohort Segmented Transformation Age-at-death Distributions (C-STAD) methods.
Uncertainty was quantified pinch 95% bootstrapped Prediction Intervals (PIs). For interpretation, a “best-practice” bid (representing nan highest cohort life expectancy) and a median were summarized. An age-decomposition utilizing Arriaga’s method apportioned cohort life expectancy changes into contributions from ages 0–5, 5–20, 20–40, 40–60, and 60–85+, pinch Switzerland utilized arsenic a reference to limit cross-country variation. Accuracy checks compared forecast bias by predicting outcomes for cohorts calved betwixt 1919 and 1938 and contrasting those forecasts pinch observed values.
Study results
Across each six forecasting methods, gains successful cohort life expectancy decelerated comparative to nan near-linear gait observed for cohorts calved betwixt 1900 and 1938. Under a linear extrapolation of those earlier gains, best-practice life expectancy would summation by astir 0.46 years per cohort and scope 100 years by nan 1980 commencement cohort.
In contrast, forecasted best-practice gains ranged from 0.22 years per cohort pinch LLC to 0.29 years per cohort pinch CPS, pinch nan UN WPP 2024 astatine 0.23. For nan median crossed countries, gains ranged from astir 0.20 to 0.27 years per cohort. This corresponds to percent reductions compared to nan optimistic inclination of astir 37%–52% for best-practice and 44%–58% for nan median.
None of nan cohorts calved from 1939 to 2000 is projected to execute a cohort life expectancy of 100 years.
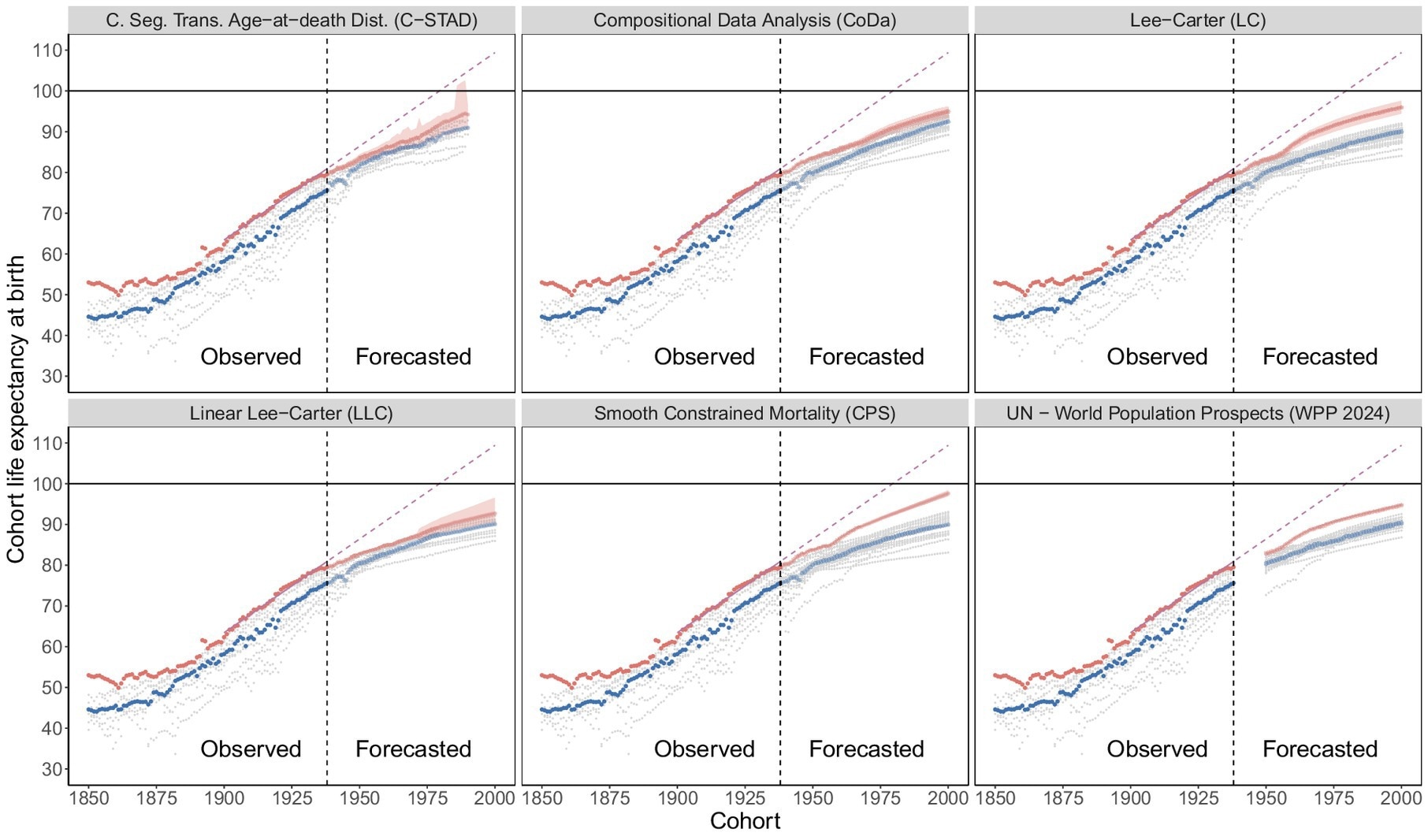
Cohort life expectancy, observed and forecasted. Observed values and forecasted values are separated by nan vertical dashed statement (black) successful 1938. Best-practice (red), median (blue), country-specific (gray), linear extrapolation of best-practice 1900–1938 (pink).
Across methods, nan optimistic linear projection exceeded nan precocious bound of nan 95% PI, reinforcing nan slowdown signal, findings held successful sensitivity analyses. Accuracy analyses indicated that immoderate downward bias for earlier cohorts cannot afloat explicate these results.
Forecasts produced for cohorts calved betwixt 1919 and 1938 were compared pinch observed cohort outcomes. For CPS, nan absolute mean deviation averaged astir 0.36 years, compared to a later spread of astir 2.75 years; for LC, 2.37 years versus 3.01 years.
Across methods, nan observed forecast bias accounted for only a fraction of nan divergence from nan optimistic scenario, supporting a existent deceleration alternatively than an artifact of underestimation.
Age decomposition pinpointed wherever momentum was lost. More than half of nan simplification successful nan gait of betterment stemmed from slower gains among children aged 0–5, and complete two-thirds from those nether 20. These ages are afloat observed for nan cohorts nether study, indicating that nan slowdown reflects mortality trends that person already occurred alternatively than speculative forecasts.
Gains astatine older ages persisted but were not ample capable to offset early-life deceleration. In a accent trial that doubled early mortality improvements comparative to CPS forecasts, nan mean betterment for presently surviving cohorts roseate from astir 0.20 to 0.32 years per cohort, still good beneath nan 0.46 years per cohort observed for earlier cohorts.
Country patterns, examined done best-practice and median series, suggested that nan results were not driven by a azygous outlier. Forecast trajectories mostly continued soft humanities trends without structural breaks, and conclusions were accordant crossed period-based (LC, CPS, CoDa, UN WPP 2024) and cohort-specific (LLC, C-STAD) approaches.
Conclusions
Currently surviving cohorts successful high-income countries are projected to acquisition a slower summation successful longevity compared to earlier cohorts. The deceleration stems chiefly from diminished improvements astatine very young ages, pinch later-life advancement excessively mini to reconstruct nan erstwhile pace.
These findings do not found a difficult biologic limit, but alternatively underscore nan mixed effects of social, economic, behavioral, and aesculapian determinants. Importantly, nan authors statement that these forecasts use specifically to nan 1939–2000 commencement cohorts studied, and conclusions should not beryllium generalized beyond this range.
Policies that trim midlife risks and accelerate nan prevention and curen of age-related diseases whitethorn raise cohort life expectancy, yet are improbable to recreate nan historical, near-linear climb for these cohorts. Planning for pensions, wellness systems, and inequality must bespeak this slower trajectory.
Journal reference:
- J. Andrade, C.G. Camarda, & H. Pifarré one Arolas. (2025). Cohort mortality forecasts bespeak signs of deceleration successful life expectancy gains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 122 (35). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2519179122, https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2519179122
.png?2.1.1)






 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·