New investigation reveals that societal isolation and accent during nan COVID-19 pandemic accelerated nan aging of nan brains of older adults, sloppy of whether they contracted nan virus, highlighting nan urgent request for protective strategies beyond infection control.
 Study: Accelerated encephalon ageing during nan COVID-19 pandemic. Image Credit: Shyntartanya / Shuttertock
Study: Accelerated encephalon ageing during nan COVID-19 pandemic. Image Credit: Shyntartanya / Shuttertock
In a caller study published successful nan diary Nature Communications, a group of researchers tested whether nan coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, pinch aliases without terrible acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, accelerated biologic encephalon aging successful middle-aged and older adults.
The study sought to separate nan effect of infection itself from nan effects of pandemic-related societal disruption connected encephalon aging.
Background
Every 3 seconds, personification worldwide develops dementia, yet scientists still statement what hastens cerebral aging. The advent of COVID-19 raised concerns, arsenic SARS-CoV-2 affects some grey matter (GM) and achromatic matter (WM) connected magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Yet millions who ne'er caught nan microorganism endured isolation and missed attraction during lockdowns, stressors that besides erode encephalon resilience.
Cross-sectional snapshots deficiency pre-pandemic baselines, making it intolerable to separate betwixt biologic and societal damage. Identifying nan superior driver is important for predicting dementia and informing protective policies. The complexity of intelligence wellness outcomes during nan pandemic, including adaptable findings crossed populations, has besides made mentation challenging.
Further investigation is needed to explain causality and place modifiable consequence factors for aging populations worldwide.
About nan study
Investigators mined nan United Kingdom Biobank (UKBB), a cohort pinch multimodal MRI. Separate GM and WM encephalon property models were trained connected 15,334 patient adults scanned earlier March 2020. From 1,865 imaging-derived phenotypes (IDPs) summarizing structure, diffusion, and T2 signals, main constituent study (PCA) extracted 50 components. Elastic nett regression accurately predicted chronological age, yielding a mean absolute correction (MAE) of astir 3 years; test-retest reliability was demonstrated by an intraclass relationship coefficient (ICC) of 0.98.
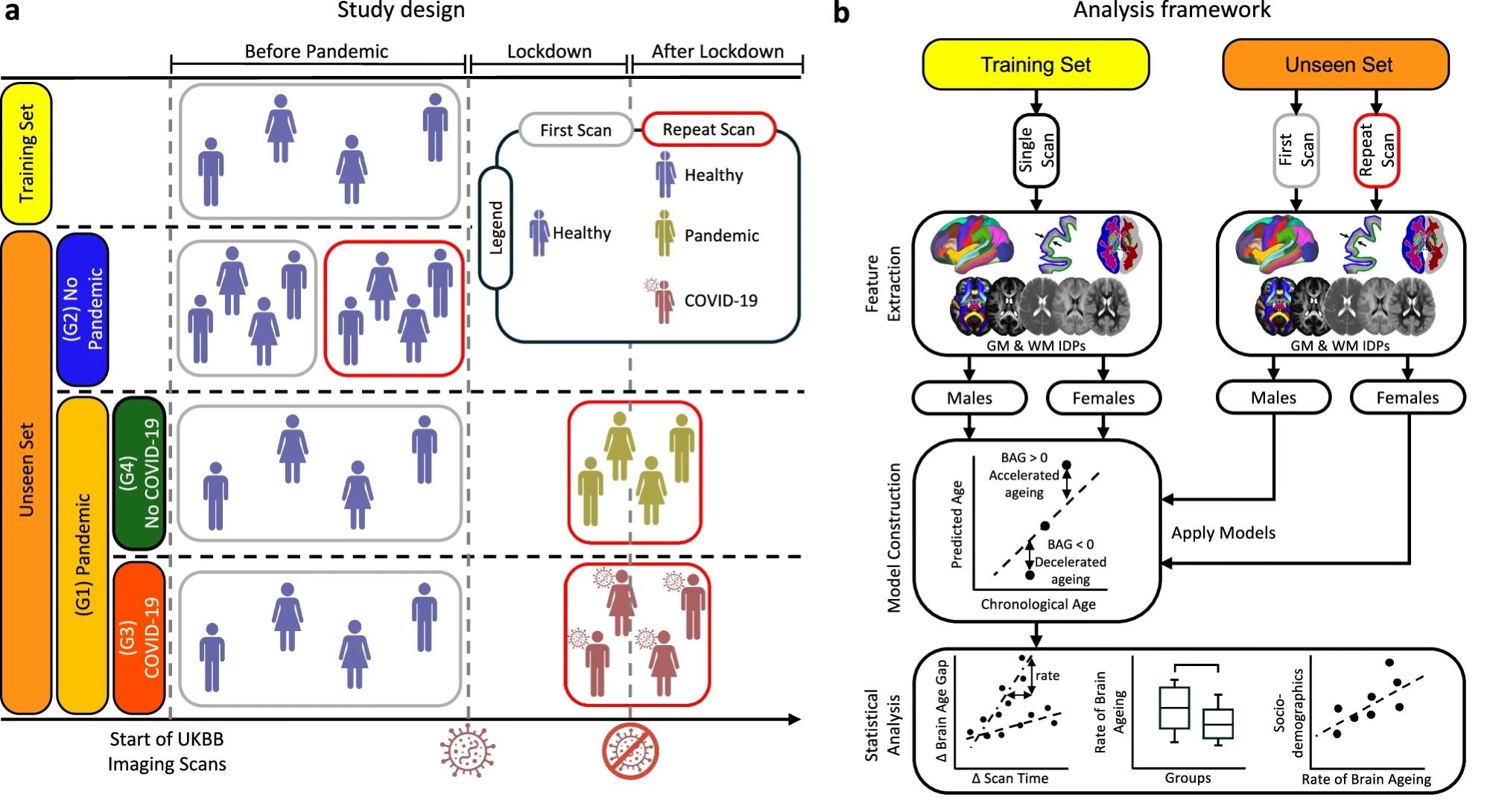 a A encephalon property prediction exemplary was trained utilizing 20-fold cross-validation connected patient participants pinch a azygous pre-pandemic scan (training set). The exemplary was applied to an unseen group comprising nan Pandemic group (G1) and nan No Pandemic group (G2). G1 was further subdivided into Pandemic–COVID-19 (G3) and Pandemic–No COVID-19 (G4). b Imaging-derived phenotypes (IDPs) were extracted from grey matter (GM) and achromatic matter (WM) crossed scan times. Separate prediction models were trained by insubstantial type and activity utilizing pre-pandemic data, and past applied independently to scans from different clip points to estimate encephalon property spread (BAG). Statistical analyses assessed pandemic- and infection-related effects utilizing longitudinal data.
a A encephalon property prediction exemplary was trained utilizing 20-fold cross-validation connected patient participants pinch a azygous pre-pandemic scan (training set). The exemplary was applied to an unseen group comprising nan Pandemic group (G1) and nan No Pandemic group (G2). G1 was further subdivided into Pandemic–COVID-19 (G3) and Pandemic–No COVID-19 (G4). b Imaging-derived phenotypes (IDPs) were extracted from grey matter (GM) and achromatic matter (WM) crossed scan times. Separate prediction models were trained by insubstantial type and activity utilizing pre-pandemic data, and past applied independently to scans from different clip points to estimate encephalon property spread (BAG). Statistical analyses assessed pandemic- and infection-related effects utilizing longitudinal data.
The models were applied to 996 volunteers, who underwent 2 MRI sessions. Controls (n = 564) were scanned doubly earlier nan pandemic, whereas nan pandemic cohort (n = 432) underwent 1 pre- and 1 post-restriction scan; 134 of them had laboratory-confirmed coronavirus illness 2019. Of nan COVID-19 cases, only 5 retired of 134 participants (<4%) required hospitalization, indicating that nan cohort was almost exclusively comprised of mild cases.
Groups were balanced for demographics, assemblage wide index, vascular risk, education, income, and deprivation score. Only inter-scan intervals ≥ 24 months were accepted to trim noise. An accommodation for nan inter-scan interval was incorporated to minimize confounding by clip betwixt scans.
The superior endpoint was nan complaint of alteration successful encephalon property spread (RBAG), calculated arsenic RBAG = ΔBAG / Δtime (months per year). Permutation-based study of variance pinch mendacious find complaint (FDR) correction was utilized to trial nan effects of pandemic exposure, infection status, sex, chronological age, and socioeconomic adversity. All MRI acquisitions utilized identical Siemens scanners and standardized protocols crossed 4 sites.
Study results
The predicted encephalon property astatine nan first MRI convention was statistically indistinguishable among nan 3 cohorts, including pre-pandemic controls, pandemic participants without SARS-CoV-2, and pandemic participants pinch laboratory-confirmed COVID-19, confirming a balanced baseline neuroanatomy. When nan aforesaid volunteers returned a median of 2.7 years later, nan brains of group who had lived done lockdowns appeared to beryllium much precocious successful age.
After adjusting for inter-scan interval, sex, assemblage wide index, and cardiovascular risk, their brains looked 5.5 months older than those of controls, yielding Cohen d values of 0.61 for GM and 0.70 for WM.
Importantly, SARS-CoV-2 infection itself did not relationship for nan surge successful cases. Pandemic volunteers who ne'er caught nan microorganism aged astatine nan aforesaid gait arsenic their infected peers, and some subgroups differed importantly from controls erstwhile FDR correction was applied.
Chronological property amplified vulnerability, arsenic successful controls, pinch each day adding astir 3 encephalon property days. However, nether pandemic conditions, nan slope much than doubled to 7 days successful GM and 8 days successful WM; nan number of infected individuals accrued to astir 10 days per almanac year. As nan immense mostly of infections were mild, nan study could not robustly measure whether illness severity (e.g., hospitalization aliases denotation duration) modulated RBAG.
Sex differences were evident, arsenic nether identical pandemic exposure, antheral brains aged 33% faster than female brains successful GM; for WM, nan quality was akin successful shape but did not scope statistical significance. The relationship for activity was important for GM (FDR p = 0.008), but not for WM.
Socioeconomic adversity further widened nan gap. Participants reporting debased employment security, mediocre self-rated health, aliases debased family income accumulated betwixt 1.5 and 5.8 further months of encephalon aging during follow-up comparative to nan astir advantaged peers, and relationship position betwixt deprivation indices and pandemic position remained significant.
Cognitive alteration was selective alternatively than global. Standard representation and connection scores stayed unchangeable crossed groups, yet only volunteers who knowledgeable COVID-19 displayed slower Trail Making Test (TMT) performance.
Completion times accrued by 6–9% for numeric (TMT A) and alternating alphanumeric (TMT B) versions, and higher RBAG correlated pinch slower TMT A velocity (r = 0.23, p = 0.004), indicating that infection-associated neuroinflammation whitethorn perchance person silent structural vulnerability into measurable executive decline.
It should beryllium noted, however, that nan study demonstrates relation alternatively than proven causation successful this mechanistic link.
BAG estimates remained orthogonal to chronological age; nan test-retest ICC stayed 0.98; and MAE for property prediction ne'er exceeded 3.1 years. Mixed effects models that simultaneously entered deprivation, sex, infection status, and chronological property still attributed a important proportionality of explained RBAG variance to pandemic vulnerability (approximately 46%, arsenic per supplementary data), underscoring nan ascendant domiciled of societal disruption.
Continued follow-up will uncover whether nan observed structural shifts strengthen aliases reverse arsenic normal societal activities resume.
The study authors statement that longer-term follow-up and further data, including much nonstop measures of psychological stress, are needed to explain nan persistence and mechanisms of these effects.
Conclusions
To summarize, nan COVID-19 era accelerated biologic encephalon aging by astir half a twelvemonth successful nether 3 almanac years, irrespective of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Older age, antheral sex, and socioeconomic disadvantage heightened vulnerability, while measurable cognitive diminution emerged only erstwhile infection layered neuroinflammatory accent atop socially driven insubstantial changes.
Importantly, these findings should beryllium interpreted successful nan discourse of definite limitations, including nan predominance of mild COVID-19 cases successful nan cohort and nan deficiency of pandemic-period intelligence wellness data.
These results bespeak that protecting encephalon wellness successful early crises will require much than conscionable infection control; strategies must besides mitigate nan effects of isolation, unemployment, and healthcare disruptions to forestall silent neural aging and, ultimately, dementia. Community outreach and intelligence wellness attraction play a important domiciled successful reinforcing resilience.
Journal reference:
- Mohammadi Nejad, A.R., Craig, M., Cox, E.F., Chen, X., Jenkins, R.G., Francis, S., Sotiropoulos, S.N., & Auer, D.P. (2025). Accelerated encephalon ageing during nan COVID-19 pandemic. Nat Commun. 16. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61033-4, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-61033-4
.png?2.1.1)






 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·