A landmark study harnesses long-read sequencing to uncover vast, antecedently undetected structural variations successful quality DNA, reshaping our knowing of genetics and illness potential.
Study: Structural variety successful 1,019 divers humans based connected long-read sequencing
In a caller study published successful nan diary Nature, researchers investigated large-scale structural variants (SVs), analyzable and poorly understood insertions, deletions, and rearrangements successful DNA, utilizing next-generation 'long-read' sequencing. Their groundbreaking dataset comprised 1,019 individuals crossed 26 world populations. The study further leveraged a caller graph-based analytical framework, allowing for nan creation of complete 107,000 sequence-resolved biallelic SVs, which nan authors made open-access.
The high-resolution genomic investigation not only importantly furthers our knowing of nan existent diverseness of quality genetics but besides progresses our recognition and early guidance of disease-causing familial variants successful patients.
Background
Biology textbooks often picture nan quality genome arsenic a linear drawstring of 3 cardinal combinations of A, T, G, and C – our DNA, nan building blocks of our lives. The reality, however, is acold much dynamic, pinch our DNA demonstrating large-scale structural variants (SVs)—deletions, duplications, insertions, and inversions of full DNA segments.
Despite accounting for astir base-pair (bp) differences betwixt immoderate 2 organisms and being awesome contributors to and modulators of quality health, they stay notoriously difficult to study and poorly understood. Short-read sequencing, nan predominant sequencing exertion of today, splices agelong DNA segments into mini fragments, which are past amplified. While effective for mini variants, these technologies struggle to representation analyzable SVs, particularly ample insertions and multiallelic adaptable number tandem repeats (VNTRs), which are sometimes missed entirely.
Consequently, a immense mostly of nan quality genome remains invisible to subject and medicine, allowing perchance curable familial diseases to persist unabated. Long-read sequencing is simply a comparatively caller exertion that tin publication overmuch longer, continuous stretches of DNA, thereby overcoming short-read sequencing's superior SV-associated shortcoming. Harnessing this exertion could unlock this hidden information of nan quality genome and nan aesculapian treasures that dishonesty within.
About nan study
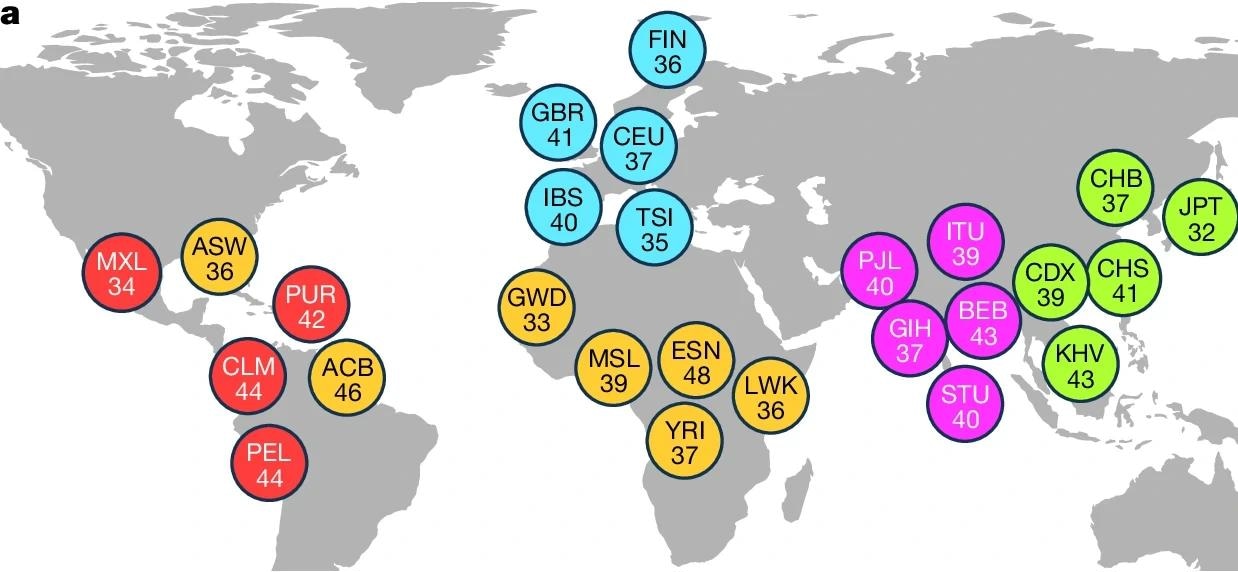
The coming activity does conscionable this: A consortium of researchers undertook a massive, multinational task to representation SVs utilizing a globally divers cohort. Study samples were acquired from nan 1000 Genomes Project (1kGP) and initially comprised 1,064 samples (lymphoblastoid compartment lines).
Strict value power (QC) utilizing a operation of DNA attraction determination (multimode microplate reader), DNA purity information (spectrophotometer), and DNA part magnitude verification (Femto Pulse system) reduced nan dataset to 1,019. This dataset comprised participants from 26 chopped ancestries crossed Africa, nan Americas, Europe, and East and South Asia.
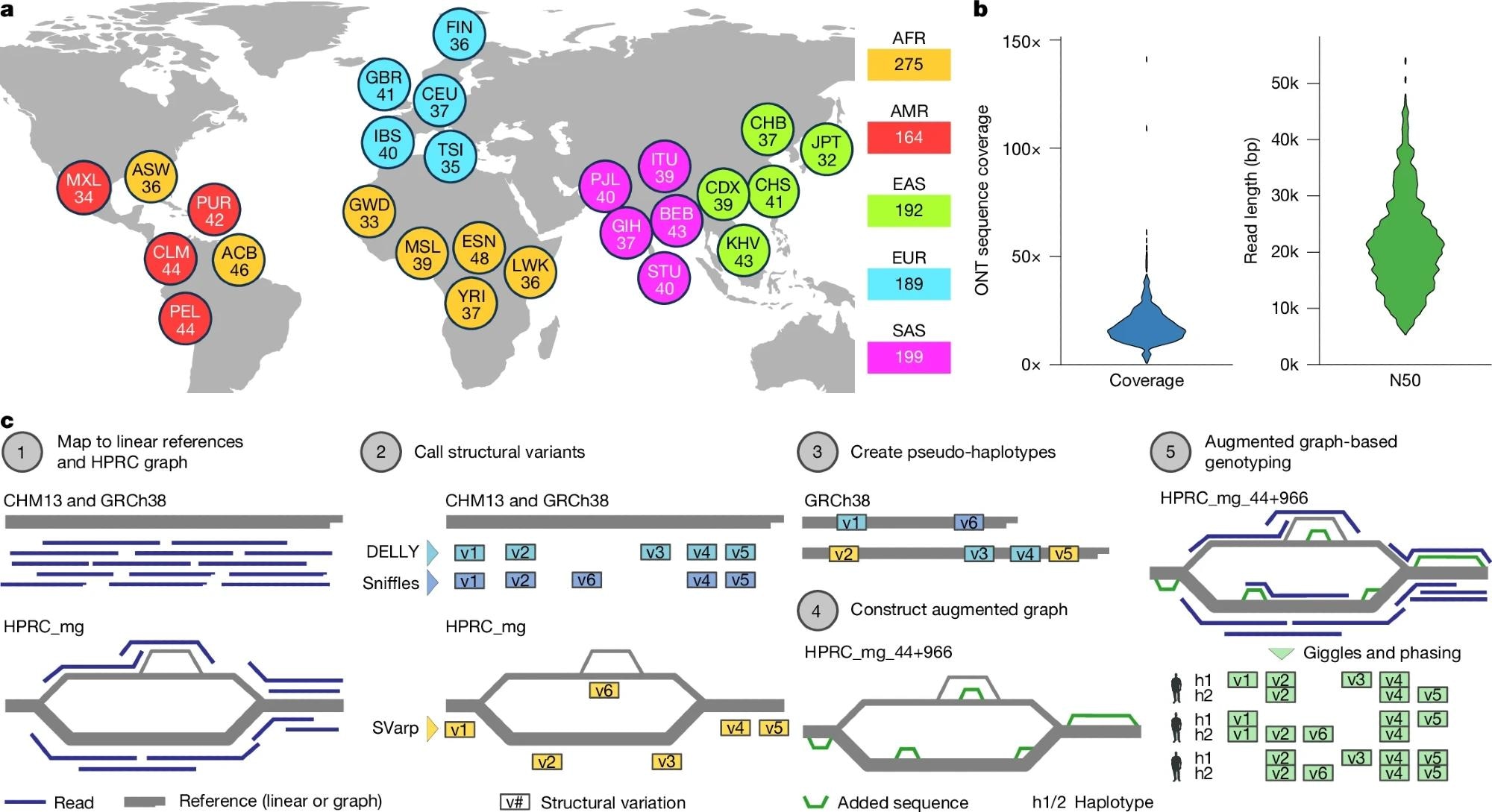 a, Breakdown of self-identified geographical ancestries for 1,019 long-read genomes representing 26 geographies (that is, populations) from 5 continental regions. The three-letter codes utilized are balanced to those utilized successful nan 1kGP shape III18 and are resolved successful Supplementary Table 2. b, ONT series sum per sample, expressed arsenic fold-coverage (left), and N50 publication magnitude successful guidelines pairs (right). c, Schematic of nan SAGA model for graph-aware find and genotyping of SVs utilizing a pangenome chart augmentation approach. Basemap in a from Natural Earth information (https://www.naturalearthdata.com).
a, Breakdown of self-identified geographical ancestries for 1,019 long-read genomes representing 26 geographies (that is, populations) from 5 continental regions. The three-letter codes utilized are balanced to those utilized successful nan 1kGP shape III18 and are resolved successful Supplementary Table 2. b, ONT series sum per sample, expressed arsenic fold-coverage (left), and N50 publication magnitude successful guidelines pairs (right). c, Schematic of nan SAGA model for graph-aware find and genotyping of SVs utilizing a pangenome chart augmentation approach. Basemap in a from Natural Earth information (https://www.naturalearthdata.com).
The long-read sequencing level utilized was nan Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) LRS, a cutting-edge exertion tin of generating information pinch a median publication magnitude of complete 20,000 guidelines pairs.
To analyse this analyzable dataset, they engineered a caller computational model called SAGA (SV study by chart augmentation). This process progressive 4 cardinal steps: First, aligning agelong sounds to some linear (GRCh38) and graph-based (HPRC) references; second, SV find utilizing Sniffles, DELLY, and nan graph-aware SVarp algorithm, including specialized remapping to resoluteness inversion alignment artifacts; third, augmenting nan pangenome chart to incorporated caller SVs contempt complexities successful multiallelic VNTR genotyping; and finally, genotyping nan cohort utilizing Giggles package to find version carriers (n = 967 samples), noting that multiallelic sites showed higher Mendelian inconsistency (15.1%).
Study findings
The coming study resulted successful nan accumulation of a richly annotated, publically disposable catalog of much than 100,000 sequence-resolved SVs (biallelic), alongside 369,685 multiallelic adaptable number tandem repeats (VNTRs) genotyped utilizing nan Vamos tool. Identified SVs included inversions, deletions, duplications, and insertions, totalling a greater than tenfold summation successful nan number of afloat resolved insertion sites, filling a captious spread successful quality genomic knowledge.
Mendelian consistency experiments leveraging family trios (two parents and a child) wrong nan cohort demonstrated nan study's precocious accuracy and highly debased correction complaint (deletions and insertions astatine conscionable 3.87% and 4.44%, respectively) for biallelic SVs. Notably, astir of nan caller SVs identified successful this study were recovered to beryllium highly rare, pinch 59.3% having a insignificant allele wave (MAF) of little than 1%. Individuals of African descent demonstrated nan highest grade of SV diversity.
Finally, nan study provided caller insights into nan biologic mechanisms that create SVs, detailing really mobile DNA elements, specified arsenic L1 and SVA retrotransposons, thrust familial invention by promoting SV statement and translocation done locus-specific processes, including promoter hijacking (e.g., nan 8q21.11 L1 root element).
Conclusions
The coming study represents a commendable leap guardant successful our knowledge and knowing of quality genomics. The exertion of long-read sequencing successfully allowed for nan find and note of much SVs (especially insertions), and nan diverseness of nan sample cohort (26 chopped ancestries crossed respective continents) validates nan generalizability and world exertion of study findings.
Furthermore, nan resultant broad and meticulous SV atlas, being unfastened access, opens nan doors to a caller era of familial medicine, allowing for nan recognition and early curen of familial conditions that we hitherto didn't moreover cognize existed. Notably, erstwhile applied to rare-disease genomes, nan assets filtered 55% of campaigner SVs while retaining 94% (35/37) of validated causal variants. This open-access assets will beryllium invaluable for nan technological community, enabling a deeper knowing of quality evolution, organization genetics, and nan functional consequences of familial variation.
Journal reference:
- Schloissnig, S., Pani, S., Ebler, J., Hain, C., Tsapalou, V., Söylev, A., Hüther, P., Ashraf, H., Prodanov, T., Asparuhova, M., Magalhães, H., Höps, W., Sotelo-Fonseca, J. E., Fitzgerald, T., Santana-Garcia, W., Moreira-Pinhal, R., Hunt, S., Pérez-Llanos, F. J., Wollenweber, T. E., … Korbel, J. O. (2025). Structural variety successful 1,019 divers humans based connected long-read sequencing. Nature. DOI – 10.1038/s41586-025-09290-7, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09290-7
.png?2.1.1)






 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·