Even little vulnerability to antagonistic societal media comments tin trigger contiguous worry and temper drops successful adults, particularly younger users, caller investigation reveals.
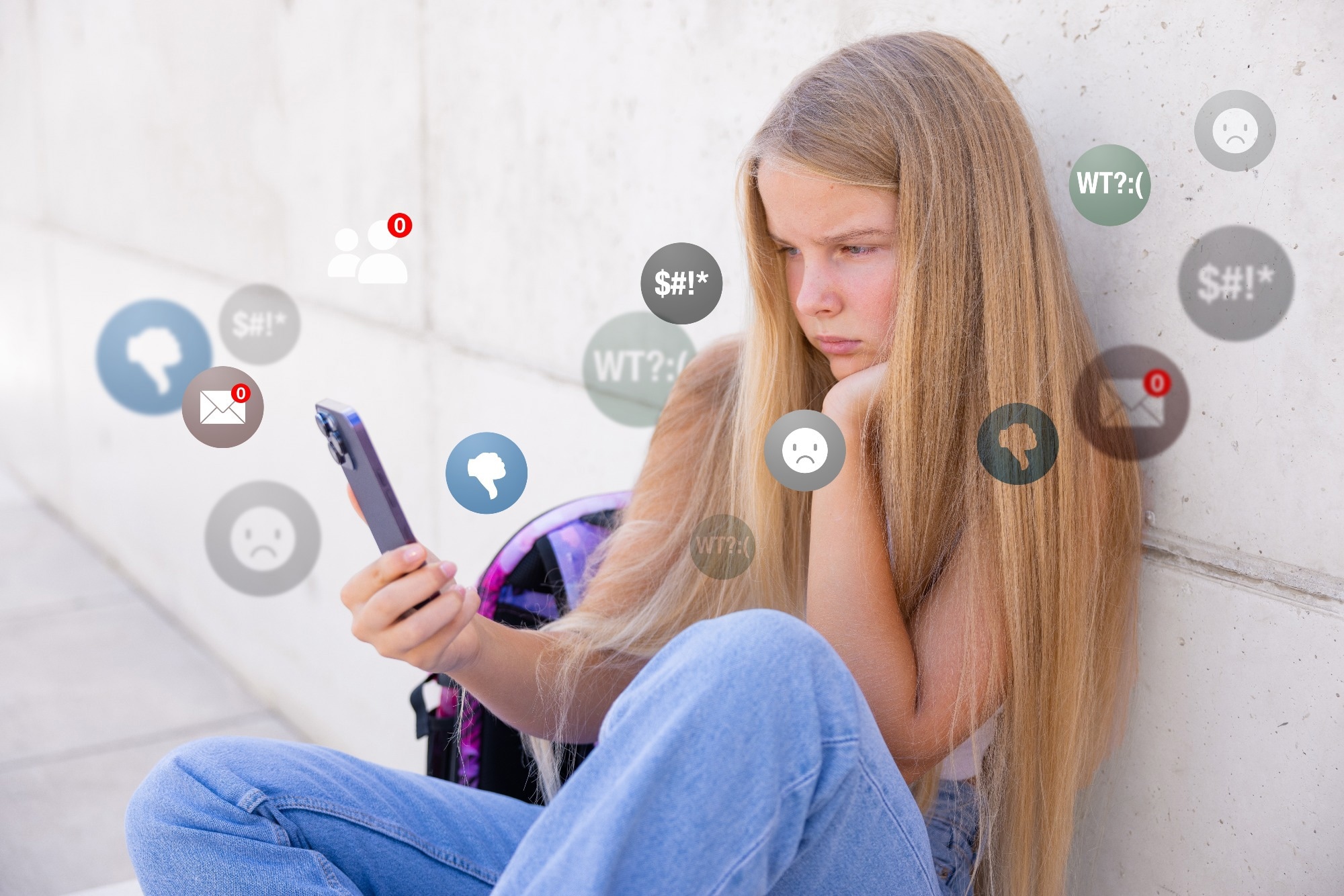 Study: An experimental online study connected nan effect of antagonistic societal media comments connected worry and mood. Image Credit: Kaspars Grinvalds / Shutterstock
Study: An experimental online study connected nan effect of antagonistic societal media comments connected worry and mood. Image Credit: Kaspars Grinvalds / Shutterstock
In a caller study published successful nan diary Scientific Reports, researchers conducted an experimental investigation to analyse nan effects of online negativity connected adults. The study leveraged artificial intelligence (OpenAI's ChatGPT) to expose big study participants to negative, neutral, aliases affirmative comments successful a simulated online forum.
Study findings revealed that reference antagonistic comments importantly accrued participants' worry levels and lowered their moods compared to different conditions. An exploratory study besides showed that younger adults (< 35 yrs) reported substantially greater worry than their older big counterparts, suggesting nan erstwhile cohort's heightened vulnerability to nan psychological toll of online interactions.
Background
Unprecedented technological innovations and nan important democratization of online accessibility person enabled societal media to scope a staggering 5.2 cardinal group worldwide. This comparatively caller relationship strategy has fundamentally reshaped quality communication, offering powerful platforms for connection, learning, and societal change.
Unfortunately, today's integer scenery is simply a double-edged sword. The aforesaid anonymity that tin empower marginalized voices besides enables and fuels nan "online disinhibition effect," wherever nan deficiency of face-to-face accountability encourages and protects perpetrators of dispute interactions, from sarcasm, shaming, and trolling to outright cyberbullying.
Since societal media platforms routinely study that younger demographics (18–29-year-olds) are their astir progressive users, a important information of nan lit investigating nan links betwixt societal media usage and intelligence wellness focuses connected this subpopulation. While this investigation has established links betwixt societal media usage and intelligence wellness challenges, a captious spread remains successful our knowing of really adults mentally respond to antagonistic online commentary.
About nan Study
The coming study intends to reside this spread by measuring nan nonstop psychological effect of antagonistic feedback connected adults successful a controlled experimental setting. The online "between-subjects" creation research quantified nan effects of antagonistic societal media comments connected big intelligence health, leveraging 2 independent variables, namely: 1. Comment type (negative vs. neutral vs. positive) and subordinate gender.
The study utilized nan online level "Prolific" to enlistee 129 study participants (85 female, mean property = 37). Participants were randomly assigned to 1 of 3 cohorts: 'positive', 'negative', aliases 'neutral'. Participants were asked to ideate themselves arsenic bloggers, and were provided paired topics (e.g., "gardening" vs. "baking") for them to blog about.
Crucially, nan blogs themselves were written by ChatGPT bots to support consistency successful penning value and length. The ChatGPT bots were past instructed to make 10 positive, neutral, and antagonistic comments for each blog that were subsequently presented to nan corresponding subordinate (dependent connected their remark cohort). Each subordinate viewed a full of 40 comments crossed 4 blog taxable choices.
Finally, participants' intelligence states were assessed utilizing nan State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI-S), a measurement of anxiety, and nan Brief Mood Introspection Scale (BMIS), which provides a snapshot of existent temper crossed various dimensions, including pleasantness and arousal.
 An illustration showing nan Building Lego blog pinch its corresponding image. From Alphacolor (2017). [White and multicolored building standard mode]. Unsplash. https://unsplash.com/photos/ipmwlGIXzcw.
An illustration showing nan Building Lego blog pinch its corresponding image. From Alphacolor (2017). [White and multicolored building standard mode]. Unsplash. https://unsplash.com/photos/ipmwlGIXzcw.
Study Findings
Results uncover a beardown statistical nexus betwixt remark type and affectional state. Specifically, participants exposed to antagonistic comments were observed to show substantially higher worry levels than those who saw neutral aliases affirmative comments, moreover erstwhile matching subordinate property crossed cohorts.
On a 4-point worry scale, participants who publication antagonistic comments scored overmuch higher (2.42) than those who publication neutral comments (1.77) aliases affirmative comments (1.55). This quality was statistically important and represented a ample effect (p < .001, ηp² = 0.256). The temper results showed nan aforesaid pattern: antagonistic comments led to little pleasant temper scores (2.37) compared to neutral (3.05) and affirmative comments (3.25).
While gender effects connected worry showed a inclination toward value (p = .099), they did not scope statistical significance, contrary to what nan investigation squad initially hypothesized. However, antheral participants did study importantly higher arousal levels than females overall. Furthermore, an unplanned exploratory study revealed that nan researchers discovered an unexpectedly wide property scope successful their sample (18–73 years). When they divided participants astatine nan median property of 35, they recovered that "younger" group (under 35 years) participants acquisition importantly higher worry (p = .011) and little pleasant moods (p = .026) crossed nan committee than their "older" group (35–73 years) counterparts, suggesting nan formers' greater wide sensitivity to harmful societal media exposure.
Conclusions
The coming study provides experimental grounds establishing nan nonstop and measurable adverse impacts of antagonistic online comments connected big intelligence health. Adults exposed to antagonistic feedback connected blog posts (that they didn't moreover write) demonstrated an contiguous driblet successful their moods and an summation successful their worry levels. While men and women responded likewise connected astir measures, younger adults were recovered to beryllium acold much susceptible to antagonistic comments, perchance owed to their ongoing shape of personality formation, making them much delicate to societal information and criticism.
However, nan study has important limitations. The usage of AI-generated comments whitethorn not afloat seizure nan complexity of basal societal media interactions, which often see elements for illustration emojis and much divers content. Additionally, nan sample consisted chiefly of English-speaking participants, apt from Western taste backgrounds, which whitethorn limit nan generalizability of findings to different populations.
This investigation highlights nan value of processing targeted strategies to mitigate nan adverse effects of online negativity. It suggests nan request for improved integer literacy programs and level features that empower users (particularly younger ones) to negociate their online situation and buffer themselves against nan inevitable sting of antagonistic interactions polluting societal media. The study was pre-registered, and each materials are disposable connected nan Open Science Framework, strengthening nan research's credibility and transparency.
Journal reference:
- Ai, Y., & von Mühlenen, A. (2025). An experimental online study connected nan effect of antagonistic societal media comments connected worry and mood. Scientific Reports, 15(1). DOI -- 10.1038/s41598-025-10810-8. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-10810-8
.png?2.1.1)






 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·