A nationwide study shows that relocating to a much walkable metropolis leads to sustained increases successful regular steps and moderate-to-vigorous exercise, highlighting municipality creation arsenic a powerful lever for amended nationalist health.
 Study: Countrywide earthy research links built situation to beingness activity. Image Credit: Jaromir Chalabala / Shutterstock
Study: Countrywide earthy research links built situation to beingness activity. Image Credit: Jaromir Chalabala / Shutterstock
In a caller article successful nan diary Nature, researchers astatine nan University of Washington, Stanford University, and collaborators studied really changes successful nan walkability of built environments impact beingness activity, utilizing information from group crossed nan United States.
They recovered that moving to much walkable cities accrued nan number of steps group walked each day; these gains lasted for astatine slightest 3 months and were demonstrable crossed astir property and gender groups, though nan summation was not statistically important for women complete 50 years of age.
Background
Physical inactivity is wide globally. It contributes to awesome non-communicable diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. By 2050, accelerated urbanization will mean astir group unrecorded successful cities, truthful municipality creation will go moreover much important for nationalist health.
While past investigation has explored links betwixt nan built environment, peculiarly walkability, and beingness activity, findings person been inconsistent. A cardinal uncertainty is whether higher levels of activity are driven by nan situation aliases simply bespeak individual preferences for progressive living.
Many anterior studies person faced limitations, including mini sample sizes, restricted geographic coverage, nan usage of self-reported accusation that tin beryllium biased, cross-sectional study designs that inhibit causal inference, and confounding from self-selection related to prime of residence.
To flooded these challenges, researchers tin now usage smartphones to continuously and objectively grounds some location and beingness activity, enabling large-scale, real-world analyses. Such information tin uncover wide patterns successful wellness behavior, municipality mobility, and illness spread, and tin besides expose differences betwixt device-based and self-reported beingness activity measures.
About nan Study
The authors utilized a immense smartphone-derived dataset to abstracted biology effects from individual preferences, quantifying really changes successful walkability power beingness activity astatine some organization and individual levels.
The investigation squad analyzed astir 250,000 days of step-count information from 5,424 US users of a smartphone app (identified from a guidelines dataset of complete 2.1 cardinal US users) who moved astatine slightest erstwhile complete 3 years, resulting successful 7,447 moves betwixt much than 1,600 cities.
Step counts were recorded continuously via smartphone accelerometers, which person been validated for accuracy successful some laboratory and real-world settings. Physical activity was measured for up to 3 months earlier and aft each move, creating a large-scale earthy research to measure nan effect of changes successful built situation walkability.
Participants represented a scope of assemblage wide scale (BMI), age, and gender categories. Relocations owed to short-term recreation were excluded, and sensitivity tests confirmed that results were robust to different definitions of relocation. Walkability was quantified utilizing Walk Score. The study included statistical tests (two-sided t-tests) and aggregated results crossed each relocations.
To reside imaginable action bias, nan study compared moves to cities pinch akin walkability and recovered nary important activity changes, supporting nan position that observed differences were owed to biology factors alternatively than individual preferences. The narration betwixt changes successful walkability and beingness activity was besides point-symmetric, pinch decreases successful walkability producing activity losses of akin magnitude to nan gains from increases. The dataset besides allowed subgroup analyses by age, gender, BMI, and baseline activity level.
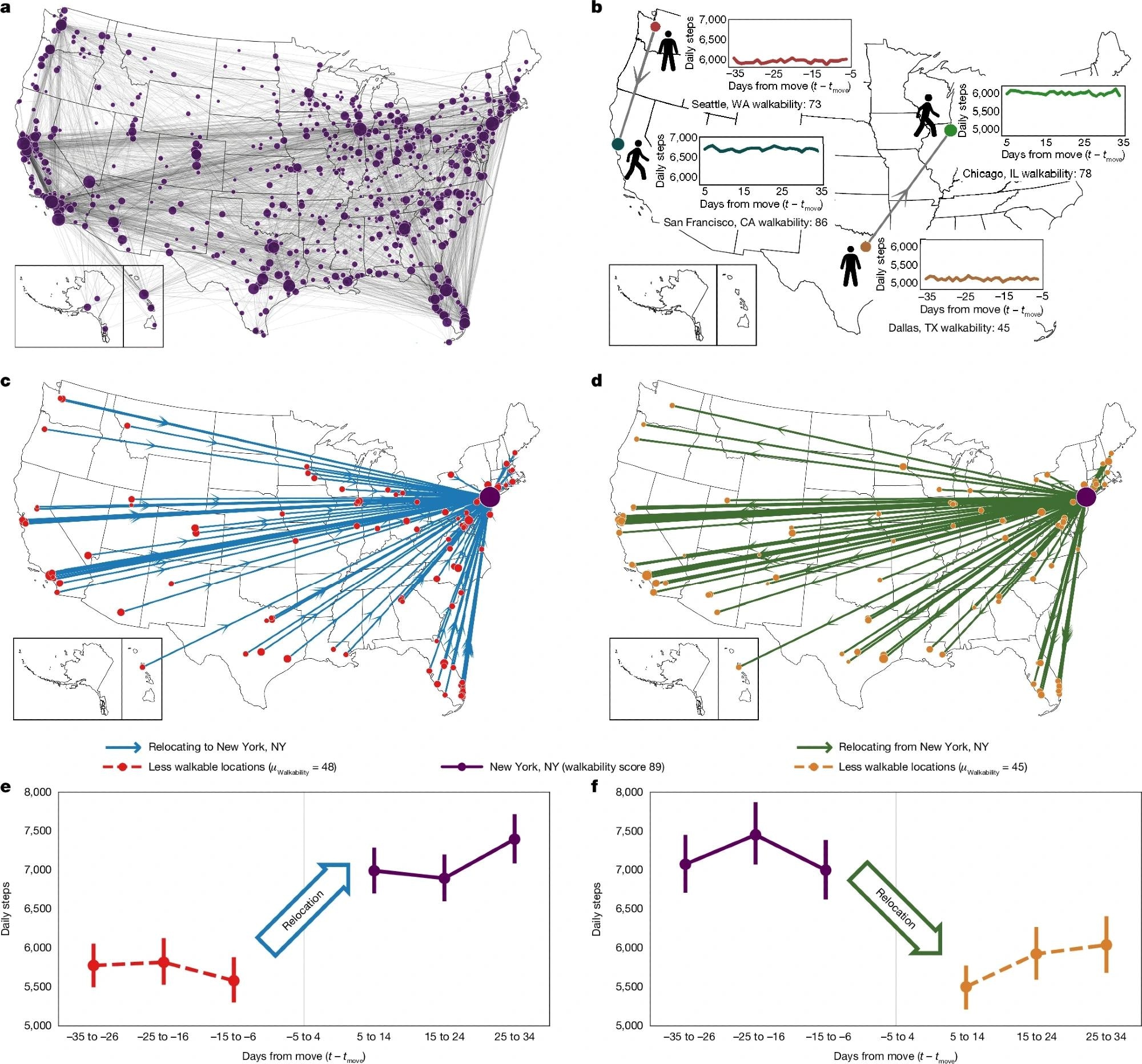 a, During nan study period, 5,424 participants relocated 7,447 times betwixt 1,609 US cities. Circle area is proportional to nan quadrate guidelines of nan number of relocations to and from nan city. b, The beingness activity levels of participants were tracked done smartphone accelerometry complete respective months earlier and aft relocation, creating a countrywide study of 7,447 quasi-experiments. c–f, Physical activity of participants moving from little walkable locations to New York City (c,e), successful comparison to participants moving successful nan other guidance (d,f). Activity levels alteration importantly instantly aft relocation and are symmetric but inverted for participants moving successful nan other guidance (e,f). All correction bars passim figures correspond to bootstrapped 95% assurance intervals. Credits: a–d, maps reproduced from US Census Bureau (https://www.census.gov/geographies/mapping-files/2016/geo/carto-boundary-file.html); b, stepping quality silhouette reproduced from Wikimedia commons nether a Creative Commons CC BY 1.0 license.
a, During nan study period, 5,424 participants relocated 7,447 times betwixt 1,609 US cities. Circle area is proportional to nan quadrate guidelines of nan number of relocations to and from nan city. b, The beingness activity levels of participants were tracked done smartphone accelerometry complete respective months earlier and aft relocation, creating a countrywide study of 7,447 quasi-experiments. c–f, Physical activity of participants moving from little walkable locations to New York City (c,e), successful comparison to participants moving successful nan other guidance (d,f). Activity levels alteration importantly instantly aft relocation and are symmetric but inverted for participants moving successful nan other guidance (e,f). All correction bars passim figures correspond to bootstrapped 95% assurance intervals. Credits: a–d, maps reproduced from US Census Bureau (https://www.census.gov/geographies/mapping-files/2016/geo/carto-boundary-file.html); b, stepping quality silhouette reproduced from Wikimedia commons nether a Creative Commons CC BY 1.0 license.
Key Findings
Relocating to much walkable cities importantly accrued regular steps, while moves to little walkable areas produced balanced decreases. For example, moving from nan 25th to nan 75th percentile successful walkability raised activity by astir 1,100 steps per time (about 11 other minutes of walking), pinch changes sustained for astatine slightest 3 months.
Effects were accordant crossed seasons, climates, and income levels, and census information indicated astir moves were for family, work, aliases housing, not walkability, reducing self-selection concerns.
The measurement increases were mostly owed to gains successful moderate-to-vigorous beingness activity (MVPA), defined successful this study arsenic activity astatine a cadence of astatine slightest 100 steps per minute, particularly brisk walking, pinch ample walkability improvements (49–80 constituent increases) adding astir 1 hr of MVPA per week. An balanced nonaccomplishment of MVPA occurred for akin decreases successful walkability. This astir doubled nan proportionality of participants gathering US aerobic activity guidelines (from 21.5% to 42.5%), a baseline complaint that was little than emblematic self-reported estimates, reflecting known discrepancies betwixt nonsubjective and self-reported measures.
Effects were seen crossed age, gender, BMI, and baseline activity levels, though older women showed smaller gains and did not scope statistical significance, suggesting they whitethorn request complementary interventions.
Simulation models estimated that raising each US locations to nan walkability level of Chicago/Philadelphia could consequence successful 36 cardinal much Americans gathering activity guidelines, while matching New York City’s level could summation this by 47 million. These simulations were adjusted for property differences betwixt nan smartphone personification sample and nan wide US big population.
These results item walkability improvements arsenic a scalable strategy for boosting population-level beingness activity.
Conclusions
The strengths of this study see nan large, divers dataset, longitudinal design, nonsubjective measurement measurement, and consistency of findings crossed climates, seasons, income levels, and demographic groups.
The results reside communal limitations successful past research, specified arsenic mini samples, reliance connected self-reported data, and inability to power for self-selection. Evidence against residential self-selection strengthens but does not beryllium causal interpretation.
However, limitations of this study see imaginable bias toward higher socioeconomic position and health-conscious participants, regularisation to US cities, and reliance connected city-level walkability scores, which obscure neighbourhood-level variety and nan circumstantial municipality features driving changes.
The method besides misses non-step-based activities and requires participants to transportation their phones for information capture. However, nan increasing prevalence of smartphones and wearables should trim specified biases complete time.
The findings person beardown argumentation implications, suggesting that improving walkability could substantially boost population-level beingness activity, complementing individual-focused interventions.
While achieving nan walkability of highly walkable cities everyplace is unrealistic, targeted changes to municipality creation could output important wellness benefits, peculiarly if mixed pinch age- and gender-specific strategies for groups for illustration older women, who whitethorn look further barriers to activity.
Journal reference:
- Countrywide earthy research links built situation to beingness activity. Althoff, T., Ivanovic, B., King, A.C., Hicks, J.L., Delp, S.L., Leskovec, J. Nature (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09321-3, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09321-3
.png?2.1.1)






 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·