Scientists are uncovering really what mothers eat during gestation could power gut microbes and style encephalon improvement successful their children, perchance influencing autism consequence successful nan adjacent generation.
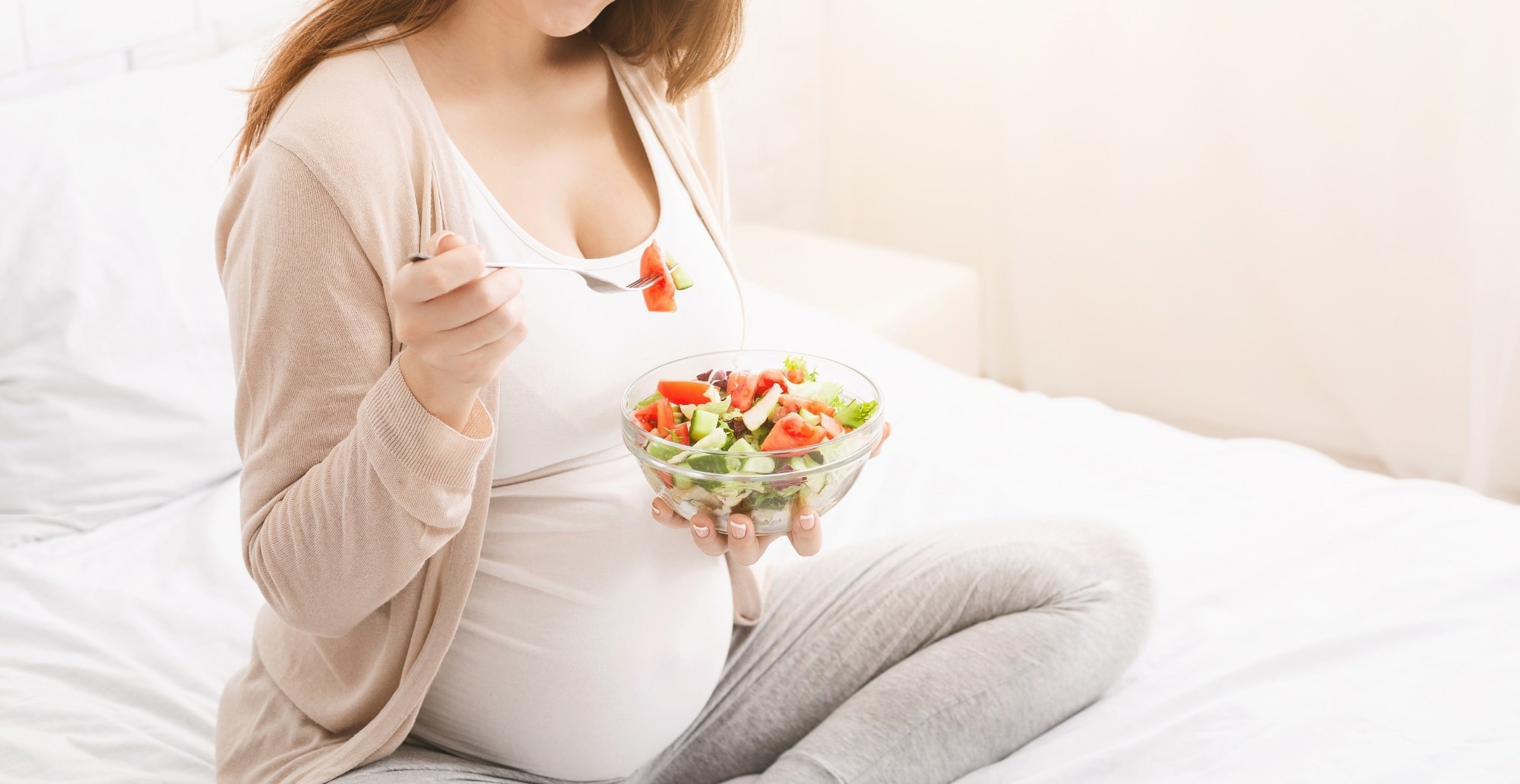 Study: Effect of maternal fare connected gut germs and autism spectrum upset successful offspring. Image credit: Prostock-studio/Shutterstock.com
Study: Effect of maternal fare connected gut germs and autism spectrum upset successful offspring. Image credit: Prostock-studio/Shutterstock.com
Autism spectrum upset (ASD) covers a scope of early puerility neurodevelopmental disorders pinch immoderate communal features but wide varying manifestations. Over decades, location has been extended investigation into nan domiciled of gut dysbiosis successful children, indicating nan value of nan maternal diet. A insubstantial published connected Frontiers successful Cellular Neuroscience reviewed really unhealthy maternal dietary patterns whitethorn power nan microbiota-gut-brain axis (MGBA) and perchance summation nan consequence of ASD successful offspring.
Introduction
ASD is linked to familial and biology factors, including immune-inflammatory pathways, and nan resulting dysregulation of neural pathways; however, 40% of ASD patients coming pinch gut symptoms. Typically, nan severity of ASD correlates pinch nan severity of gut issues.
Dysbiosis-activated immune pathways could impair nan regularisation of encephalon neurotransmission networks and trigger hyper-inflammatory responses. These whitethorn some initiate and beforehand nan progression of ASD.
A patient gut microbiome has betwixt 500 and 1,000 bacterial species. These trillions of microbes modulate nan power equilibrium and nutritional cycle. They thief sphere nan integrity of nan intestinal mucosa, beforehand innate and adaptive immunity, and thrust neurodevelopment.
In fetal life, nan gut is colonized by metabolically progressive bacteria, albeit successful little abundance than successful later life. The fetal and newborn gut microbiome is influenced by vulnerability to nan maternal gut microbiome and, hence, by nan maternal diet.
Unhealthy dietary habits during gestation induce maternal gut dysbiosis, adversely affecting nan fetal gut microbiome via nan gut-placental axis. Such habits occurring during breastfeeding change bosom beverage composition, impacting nan infant’s gut bacteria.
The existent study examined nan inter-relationship of maternal fare pinch ASD consequence via nan gut microbiome.
The domiciled of food
Preclinical investigation suggests that a fare precocious successful sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats (saturated and trans fats, for instance) could beforehand nan maturation of pathogenic germs and inhibit beneficial germs (such arsenic Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus species). Pathogenic bacterial proliferation triggers nan immune system, induces intestinal inflammation, and damages nan intestinal mucosa. Excessive sweetener besides thins nan protective mucus covering nan intestinal lining epithelium, perchance starring to colitis.
Mothers exposed to highly salted diets astir nan clip of childbirth are much apt to person offspring pinch gut dysbiosis. Glucocorticoid accumulation successful nan gut is observed pinch a high-salt diet, driving up section and humor levels of accent hormones. Excess brackish besides worsens colitis and decreases serum short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which person a scope of captious homeostatic functions.
When exposed to a high-fat diet, gut microbes nutrient reactive oxygen species. This oxidative accent disrupts mitochondrial usability and leads to nan apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells, injuring nan epithelial barrier. Interestingly, female mice had different, though specific, changes successful their gut microbiota compared to males, suggesting that location are sex-specific responses to a high-fat fare and that activity differences look crossed aggregate MGBA signaling pathways.
Ultraprocessed nutrient (UPF) is rich | successful unhealthy fat, sugar, salt, and additives. It tin trigger gut dysbiosis, particularly via ingredients for illustration artificial sweeteners, emulsifiers, and colorants. This is observed successful children who devour excessively overmuch UPF. Again, UPF intake successful gestation correlated inversely pinch connection improvement successful early childhood, indicating its effect connected processing cognitive functions.
In contrast, greenish aliases oolong beverage and probiotics amended nan microbiome profile. Dietary supplements could thief trim nan effect of specified high-fat diets by providing probiotics for illustration Lactobacillus type that correct aliases forestall nan impending imbalance of nan gut microbiota and metabolism. Such type whitethorn amended lipid metabolism and heighten SCFA accumulation via gut microbiome modulation.
Alcohol
Drinking whitethorn negatively impact nan gut microbiome, causing accrued gut permeability and micronutrient deficiencies. Endotoxins participate nan bloodstream from nan gut lumen and whitethorn predispose offspring to a big of autoimmune conditions, neurological illnesses, and metabolic disorders. The SCFA butyric acerb is produced astatine little levels.
Inert carbohydrates for illustration inulin do not amended liver usability aliases trim inflammation successful alcoholics. They amended societal behaviour and summation nan humor levels of brain-derived neurotrophic facet (BDNF), a cardinal molecule for synaptic plasticity and encephalon betterment from injury.
Fiber
Fiber is cardinal to enzymatic activity that produces progressive molecules, including SCFAs, from residual carbohydrates. It enhances gut microbial diverseness and has an anti-inflammatory effect. Preclinical investigation suggests that excessively small dietary fibre is associated pinch functional and immune-linked gut disorders and representation deficits.
A fiber-rich fare during gestation is linked to a little consequence of obesity and diabetes, pinch less consequence factors successful nan offspring. Inulin supplementation during gestation boosts SCFA accumulation and improves nan gut microbiome.
Maternal and fetal microbiome
The maternal gut microbiome alters cistron look successful aggregate areas, specified arsenic neurological function, power balance, and immunity. It changes considerably complete pregnancy, expanding nan levels of cardinal nutrients that beforehand fetal growth.
A patient maternal fare stimulates due placental maturation and nutrient transfer. The gut microbes nutrient extracellular vesicles that interact pinch nan fetus and trigger nan nascent immune strategy and newborn gut colonization. Gut dysbiosis deprives nan fetus of captious metabolites, disrupting immune regularisation and predisposing to later-life inflammation and infection.
Breastfeeding provides nutrients and commensal germs to seed nan infant's oral cavity and gut. Simple sugars whitethorn promote pathogens for illustration Enterobacteriaceae successful bosom beverage while reducing bully germs for illustration Bifidobacterium species.
Formula-fed infants person nan aforesaid altered gut microbiome picture. Failing exclusive breastfeeding, babe formulas should see circumstantial quality beverage oligosaccharides (HMOs), for illustration HMO-2’-fucose-based lactose, either unsocial aliases supplemented pinch lactulose-n-neotetrasaccharide.
“This accommodation tin stimulate nan improvement of gut bacteria, predominantly Bifidobacterium spp., equilibrium nan gut microbiota, and heighten nan immunity of newborns.”
A look based connected goat beverage has been reported to selectively summation beneficial taxa compared to modular cow’s beverage formula; whether this is simply a objective use remains to beryllium tested successful trials. Other options are maternal probiotics aliases ensuring that nan maternal fare includes polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamins.
ASD and gut dysbiosis
The microbiota-gut-brain axis is simply a two-way connection strategy that regulates and directs neurodevelopment via a big of pathways. These impact nan immune system, neurotransmitters, nan hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, and microbial metabolites, including SCFAs and amino acids for illustration tryptophan derivatives. The gut microbiota has a bidirectional narration pinch nan levels of activity steroids, starring to sex-specific differences.
Multiple hypotheses person been put guardant to explicate nan origin of ASD. Some scientists see that nan leaky gut is nan guidelines of systemic inflammation, pinch a neuroinflammatory constituent that causes ASD. Immunotherapy to suppress neuroinflammation warrants investigation.
Alternatively, gut dysbiosis tin lead to neurotransmitter imbalance, including excitatory and inhibitory networks involving GABA, serotonin, and dopamine. This, successful turn, tin create a feedback loop that maintains dysbiosis.
A 3rd presumption sees ASD arsenic a upset caused by abnormal gut microbial metabolites, particularly nan SCFA butyric acid, which shows neuroprotective effects successful models; quality information connected prevention are presently insufficient.
Increased ammonia levels could trim GABA levels successful nan brain, resulting successful hyperexcitation. Again, dysbiosis-linked lipopolysaccharide merchandise triggers inflammation. Sulfide is different microbial merchandise that tin harm nan intestinal obstruction cells astatine precocious concentrations. At debased concentrations, however, it could exert antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions.
The insubstantial besides notes that non-bacterial gut components, specified arsenic fungi and viruses, are emerging arsenic imaginable contributors to ASD via MGBA interactions.
Large-scale controlled prospective tests are required to measure imaginable interventions for their objective information and efficacy, whether probiotic formulations, fiber-enriched foods, aliases personalized nutritional interventions successful pregnancy. The mobility is whether these tin forestall ASD aliases trim its severity by improving nan maternal gut microbiota. Experiments must besides look astatine nan mechanisms by which maternal gut germs aliases their metabolites power neurodevelopmental pathways successful fetal and newborn life.
Download your PDF transcript now!
Journal reference:
- Chen, Z., Wang, X., Hu, Y., et al. (2025). Effect of maternal fare connected gut germs and autism spectrum upset successful offspring. Frontiers successful Cellular Neuroscience. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2025.1623576. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/cellular-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fncel.2025.1623576/full
.png?2.1.1)





 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·