Experts uncover really integrative particles lodged successful arteries could heighten bosom illness risk, demanding urgent attraction from clinicians and policymakers.
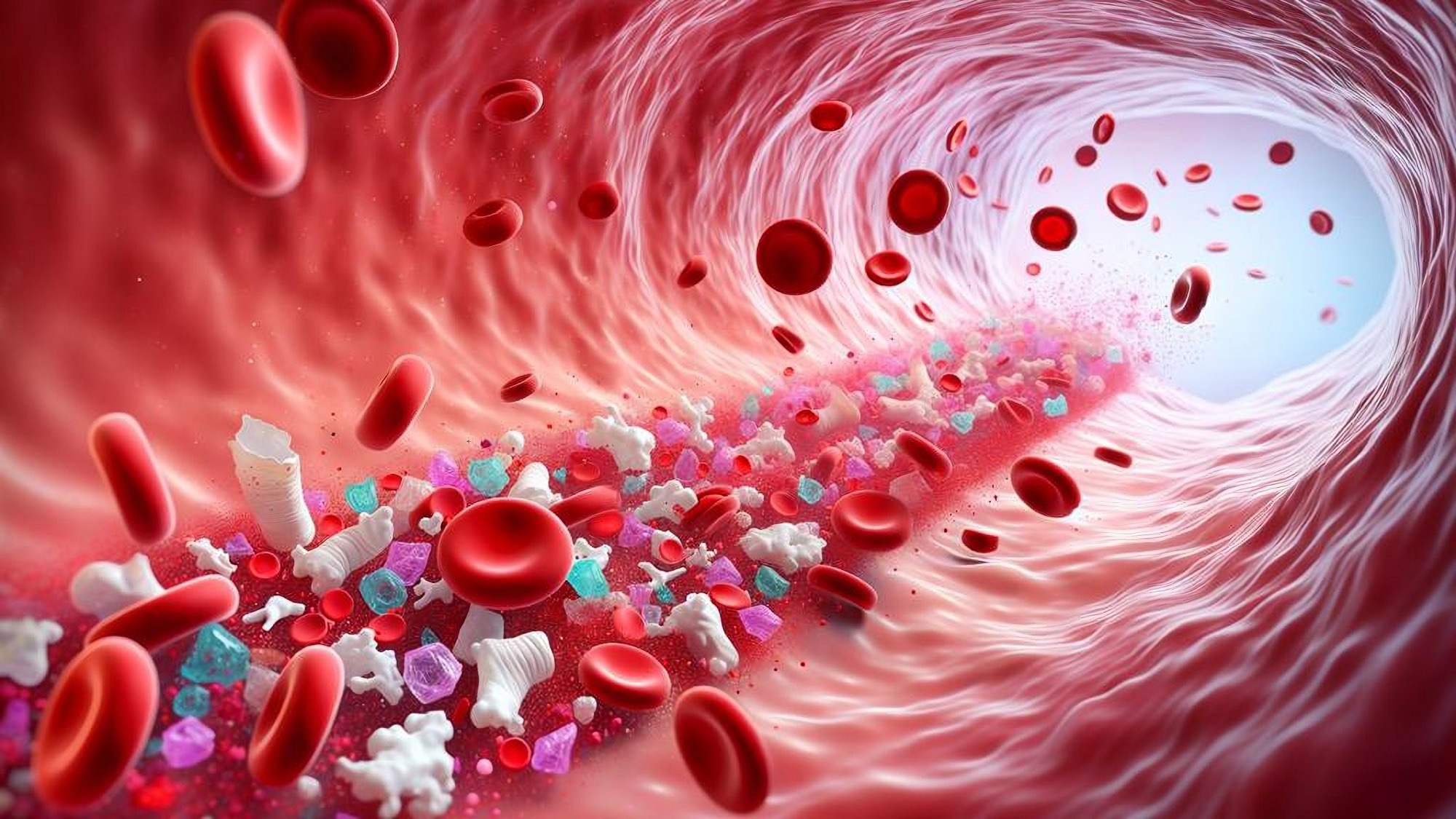
Microplastics and nanoplastics: mini threats for cardiovascular diseases? Image Credit: Shutterstock
In a caller article published successful nan journal Cardiovascular Research, researchers discussed whether nanoplastics (NPs) and microplastics (MPs) are emerging consequence factors for cardiovascular diseases (CVDs).
The ubiquity of plastics has led to an biology situation pinch profound wellness implications. While plastics were initially regarded arsenic revolutionary materials owed to their durability and versatility, they person go pervasive pollutants that part into NPs and MPs and infiltrate nan nutrient chain, ecosystem, and nan quality body. NPs and MPs person been detected successful respective quality tissues, including nan brain, blood, liver, lungs, placenta, and atheroma.
The authors first reported that NPs and MPs accumulate successful atherosclerotic plaques successful a anterior NEJM cohort study, which is associated pinch a higher consequence of cardiovascular disease. In particular, individuals pinch detectable NPs and MPs successful their plaques had an nonstop 4.5-fold accrued consequence of awesome adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) than those without. These findings, on pinch preclinical evidence, propose that NPs and MPs play an progressive domiciled successful promoting MACE aliases atherogenesis.
Furthermore, NPs and MPs whitethorn enactment arsenic carriers of toxic substances, specified arsenic pesticides, herbicides, and dense metals, which tin harm nan cardiovascular system. Indirect mechanisms specified arsenic gut microbiota dysregulation person besides been proposed. This raises caller and urgent cardiovascular investigation questions and challenges nan accepted position of atherosclerosis by introducing a caller consequence factor. However, longitudinal quality studies establishing causality are presently lacking, and extended studies pinch divers populations are needed to corroborate these findings.
Implications for translational and objective research
The beingness of NPs and MPs successful atherosclerotic plaques highlights an emergent consequence facet and mightiness require integration into prevention strategies. While cardiovascular consequence factors, including smoking, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and obesity, are good established, biology pollutants and their domiciled successful CVDs person gained important attraction successful caller years.
While nan toxic effects of aerial contamination person agelong been linked to higher cardiovascular mortality, nan find that NPs and MPs whitethorn person comparable effects implies that cardiovascular medicine must broaden its attraction besides to see biology cardiology. Whether NPs and MPs straight lend to plaque destabilization aliases formation, aliases their beingness is simply an biology vulnerability marker, remains unknown. The complexity of measuring and dosing MPs and NPs limits comparability crossed studies.
In preclinical models, NPs and MPs person been recovered to induce endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, apoptosis, pyroptosis, and vascular inflammation, suggesting that they mightiness not beryllium specified bystanders. Another basal mobility is really NPs and MPs participate nan vascular strategy and build up successful plaques. Although imaginable routes see inhalation of airborne particles, ingestion via contaminated h2o and food, and absorption done nan skin, which sources are much applicable remains unclear. Uncertainty besides exists astir which particle sizes and polymer types are astir pathogenic, pinch early hypotheses suggesting that nanoplastics whitethorn penetrate biologic barriers much readily.
Prevention strategies and therapeutic perspectives
Addressing nan cardiovascular effect of plastics necessitates some superior and secondary prevention strategies. Primary prevention efforts should attraction connected decreasing nan contamination of plastics successful nan situation and successful humans. However, this poses a important economical and governmental challenge, pinch existent regulatory measures described arsenic weak, and bequest contamination is expected to persist for astatine slightest a period moreover if accumulation were to extremity today. Secondary prevention strategies should purpose astatine alleviating nan effects of NPs and MPs successful nan quality body.
Current anti-atherosclerotic therapies whitethorn connection immoderate protection if a domiciled for NPs and MPs successful inflammation, apoptosis, and endothelial dysfunction is substantiated successful humans. Drugs specified arsenic statins, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, and proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors whitethorn counteract vascular inflammation, moreover if they do not reside nan guidelines cause. In addition, exploratory strategies to heighten gastrointestinal elimination are being considered, including dietary fibres, probiotics, and bile-acid sequestrants.
Concluding remarks
Together, NPs and MPs correspond an unprecedented situation successful CVD. They whitethorn look arsenic a caller cardiovascular consequence facet if their domiciled successful CVD improvement and atherogenesis is confirmed. A multidisciplinary approach, incorporating nationalist health, molecular biology, epidemiology, and pharmacology, whitethorn beryllium basal to reside this issue. Overall, cardiovascular medicine should accommodate to nan challenges posed by these caller biology threats.
Journal reference:
- Marfella R, Prattichizzo F, Paolisso G (2025). Microplastics and nanoplastics: mini threats for cardiovascular diseases? Cardiovascular Research, cvaf143. DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvaf143, https://academic.oup.com/cardiovascres/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cvr/cvaf143/8249089
.png?2.1.1)





 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·