Scientists uncover really targeted probiotics whitethorn thief athletes spell further, retrieve faster, and enactment healthier, if nan correct strains are chosen and investigation gaps are closed.
 Review: Probiotic supplementation for optimizing diversion performance: existent grounds and early perspectives for microbiome-based strategies
Review: Probiotic supplementation for optimizing diversion performance: existent grounds and early perspectives for microbiome-based strategies
In a caller reappraisal published successful nan diary Frontiers successful Nutrition, researchers collate and synthesize up-to-date technological knowledge to elucidate relationships and interdependencies betwixt probiotics, nan gut microbiome, and jock workout performance. The reappraisal intends to utilize this accusation to alteration athletes, their trainers, and aesculapian professionals to make informed decisions astir training techniques that optimize capacity while minimizing adverse physiological effects.
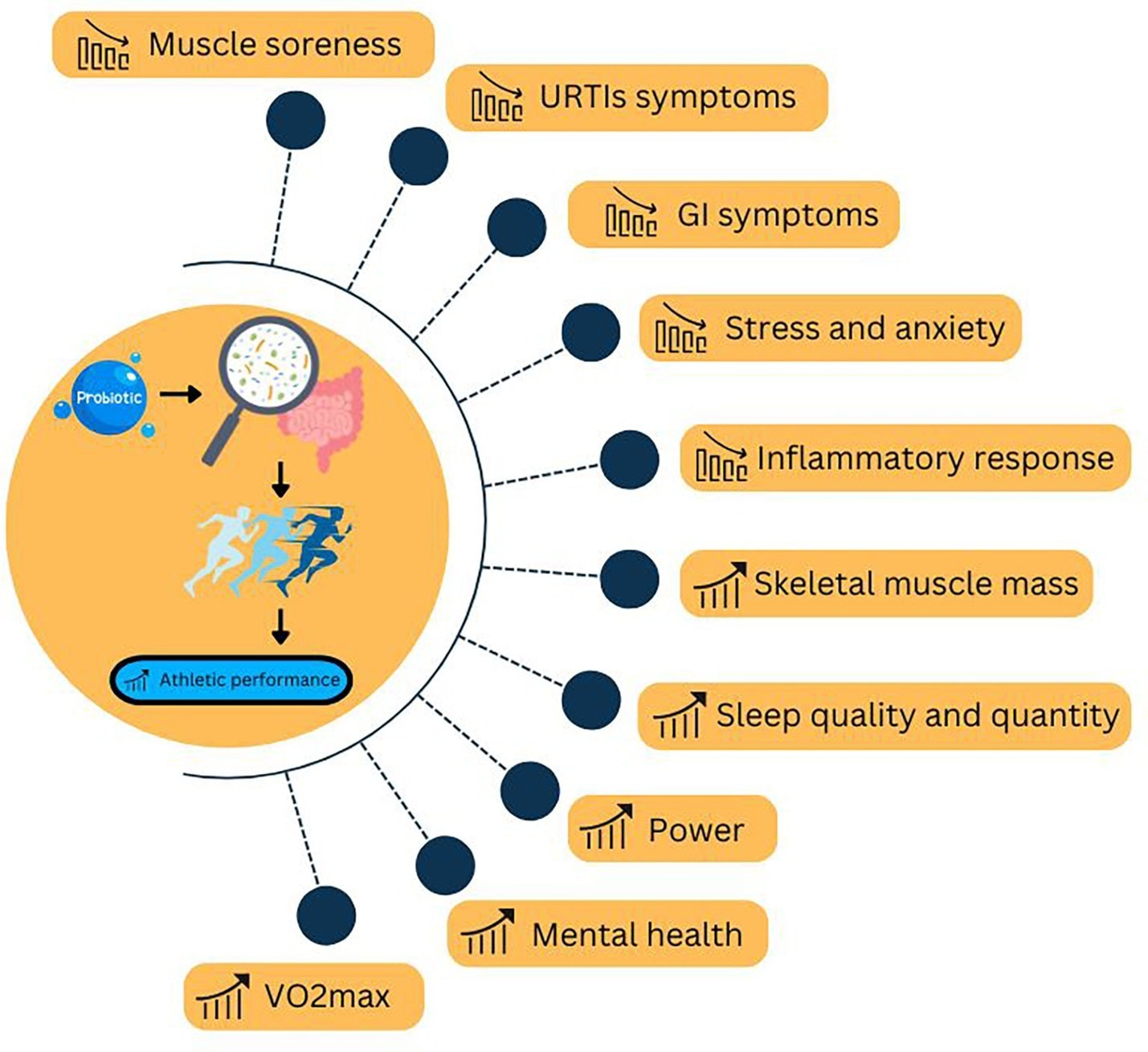
The reappraisal highlights nan multifaceted imaginable benefits of probiotic supplementation successful athletes, including modulation of inflammation, betterment successful gut obstruction function, and grounds of altered metabolic pathways. However, it cautions that nan effects are highly strain-specific, dose-dependent, and limited connected nan type of sport, and that not each studies show affirmative results. It suggests that incorporating probiotic supplementation successful diversion training plans whitethorn beryllium beneficial for immoderate athletes, but further investigation is needed earlier making cosmopolitan recommendations.
There is presently insufficient grounds to reason that probiotic supplementation is basal for preventing wounded aliases that it will consistently supply tangible capacity benefits. Current investigation is highly strain-specific and context-dependent, underscoring nan request for standardized and generalizable research, particularly for resistance-based sports.
Background
Professional elite sports are attempts astatine marginal gains, wherever athletes activity immoderate intends of enhancing capacity and recovery. Decades of investigation person established training and nutrition arsenic cornerstones of diversion development. Surprisingly, a cardinal constituent of physiological well-being (and, by extension, betterment and performance), nan trillions of microbes that comprise nan gut microbiome, remains mostly ignored successful astir accepted training regimes.
The gut microbiome is simply a analyzable ecosystem that actively contributes to nutrient absorption, immune function, and nan regularisation of inflammation, each of which are captious factors successful diversion success. Consequently, a increasing assemblage of investigation successful nutrition and sports seeks to unravel nan bidirectional associations betwixt gut microbiome properties and diversion wellness outcomes.
Specifically, this investigation intends to utilize probiotic supplements to alleviate communal jock complaints (e.g., gastrointestinal distress successful endurance runners aliases precocious respiratory tract infections that tin discuss performance) and heighten wide performance.
About nan review
The coming reappraisal intends to systematically measure nan existent technological landscape, revealing nan pros and cons of circumstantial probiotic strains, nan existent limitations of athlete-focused probiotic research, and cutting-edge ongoing investigation that whitethorn alteration athletes to push harder pinch reduced wounded consequence than ever before.
Peer-reviewed publications investigating “probiotics,” “microbiome,” and “exercise performance” betwixt 2015 and 2024 were identified done a civilization keyword hunt of PubMed and Scopus databases. All identified publications were subjected to title, abstract, and full-text screening, pinch some animal and quality tests included successful reappraisal outcomes.
Review outcomes were classified into 3 categories to amended proposal specificity: 1. Endurance-based sports, 2. Intermittent-exercise sports, and 3. Resistance training. For each category, nan reappraisal synthesizes a clear overview of what is known, what is promising, and wherever captious gaps successful our knowledge remain. The reappraisal besides discusses a 4th group, wheelchair athletes, arsenic an understudied organization regarding probiotic supplementation.
Review findings
Endurance athletes
This subcategory of athletes (runners, cyclists) is nan champion studied from nan gut microbiome lens. The reappraisal reveals that exercise-induced gastrointestinal distress is nan astir communal physiological interest among endurance athletes. Encouragingly, respective studies leveraging multi-strain probiotic supplements person reported important decreases successful GI symptoms pursuing supplementation.
Specific probiotic strains person been further linked to nonstop capacity enhancement. For example, supplementation pinch Bifidobacterium lactis BL-99 successful cross-country skiers improved lipid metabolism and VO₂ max. Similarly, a 16-week study connected roadworthy cyclists utilizing a multi-strain look reported improved aerobic capacity and clip to exhaustion successful immoderate measures, while different studies recovered nary important effects connected VO₂ max aliases clip to fatigue.
Mechanistic evaluations property these observed benefits to reduced systemic inflammation (lower levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines for illustration TNF-α and IL-6) and mitigated oxidative stress. However, not each studies person demonstrated affirmative effects, and immoderate person shown nary important changes successful cardinal capacity outcomes. Additionally, nan reappraisal discusses mechanistic pathways, specified arsenic nan gut–liver axis and gut–brain axis, which whitethorn mediate immoderate of nan observed physiological effects.
Importantly, a 6-week involution successful shot players utilizing a synbiotic (probiotic + prebiotic) was associated pinch a boosted maximal bosom complaint (HRmax) and lactic acerb elimination complaint compared to controls; however, an summation successful HRmax is physiologically counterintuitive for improved betterment and whitethorn bespeak limitations successful nan root paper’s mentation aliases reporting.
Intermittent-exercise athletes
While not arsenic extensively studied arsenic endurance athletes, intermittent-exercise athletes (e.g., shot and basketball) besides show benefits from probiotic supplementation. Notably, probiotics importantly trim nan incidence and long of precocious respiratory tract infections, thereby mitigating instances of missed training and competition. A 6-week involution successful shot players utilizing a synbiotic markedly lowered URTI symptoms while boosting HRmax and lactic acerb elimination complaint compared to controls.
Several studies person demonstrated nan intelligence wellness and mood-enhancing benefits of probiotic supplementation. A 6-week Lactobacillus casei intervention resulted successful little accent and worry levels successful badminton players, while besides improving metrics of their aerobic capacity. However, different tests successful dancers and shot players did not observe important effects connected pain, fatigue, aliases definite capacity metrics, highlighting variability successful findings.
Resistance athletes
In opposition to endurance and intermittent-exercise athletes, guidance athletes (e.g., bodybuilders) stay importantly under-researched. Limited information propose that probiotic supplementation pinch Bacillus coagulans tin heighten branched-chain amino acerb absorption and amended limb property powerfulness successful trained males, indicating imaginable benefits crossed physiology and performance. Other studies successful resistance-trained athletes study improvements successful definite spot measures and assemblage composition; however, nan results are inconsistent, and nan information are sparse. Factors specified arsenic probiotic dosage, duration, and wave of supplementation whitethorn power outcomes and require further study.
Wheelchair athletes
Wheelchair athletes correspond an understudied organization pinch unsocial challenges. Limited grounds suggests that probiotic supplementation whitethorn trim inflammatory markers and amended gut microbiome diversity; however, nan findings are mixed, pinch immoderate studies showing reduced inflammation but nary important betterment successful gastrointestinal symptoms.
Conclusions
Probiotic supplementation is simply a promising but nuanced strategy for athletes. The reappraisal emphasizes that a one-size-fits-all attack is ineffective, pinch benefits being highly strain-specific, dose-dependent, and tied to nan demands of nan sport. While endurance and intermittent-sport athletes tin summation measurable advantages successful gut health, immunity, and aerobic performance, existent information are insufficient for those successful spot and powerfulness sports.
Some studies study nary important improvements successful cardinal capacity aliases wellness measures, underlining nan request for further robust, standardized investigation to found the efficacy of probiotics successful sports settings. Future studies should explicitly archive supplementation protocols and explain mechanistic pathways specified arsenic gut–brain and gut–liver axis modulation.
Future investigation should standardize methodologies, attraction connected circumstantial strains, and elucidate nan precise mechanisms (e.g., neurotransmitter production) of probiotic interactions, enabling evidence-based sports plans. At present, probiotic supplementation shows committedness but should not beryllium considered a guaranteed aliases cosmopolitan strategy for optimizing diversion capacity until much conclusive grounds is available.
Journal reference:
- Teglas, T., & Radak, Z. (2025). Probiotic supplementation for optimizing diversion performance: existent grounds and early perspectives for microbiome-based strategies. Frontiers successful Nutrition, 12. DOI 10.3389/fnut.2025.1572687. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/nutrition/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1572687/full
.png?2.1.1)






 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·