From chestnut to manuka, chromatic varieties show neuroprotective powerfulness successful laboratory studies against Alzheimer’s disease, but scientists accent that only quality tests tin uncover real-world benefits.
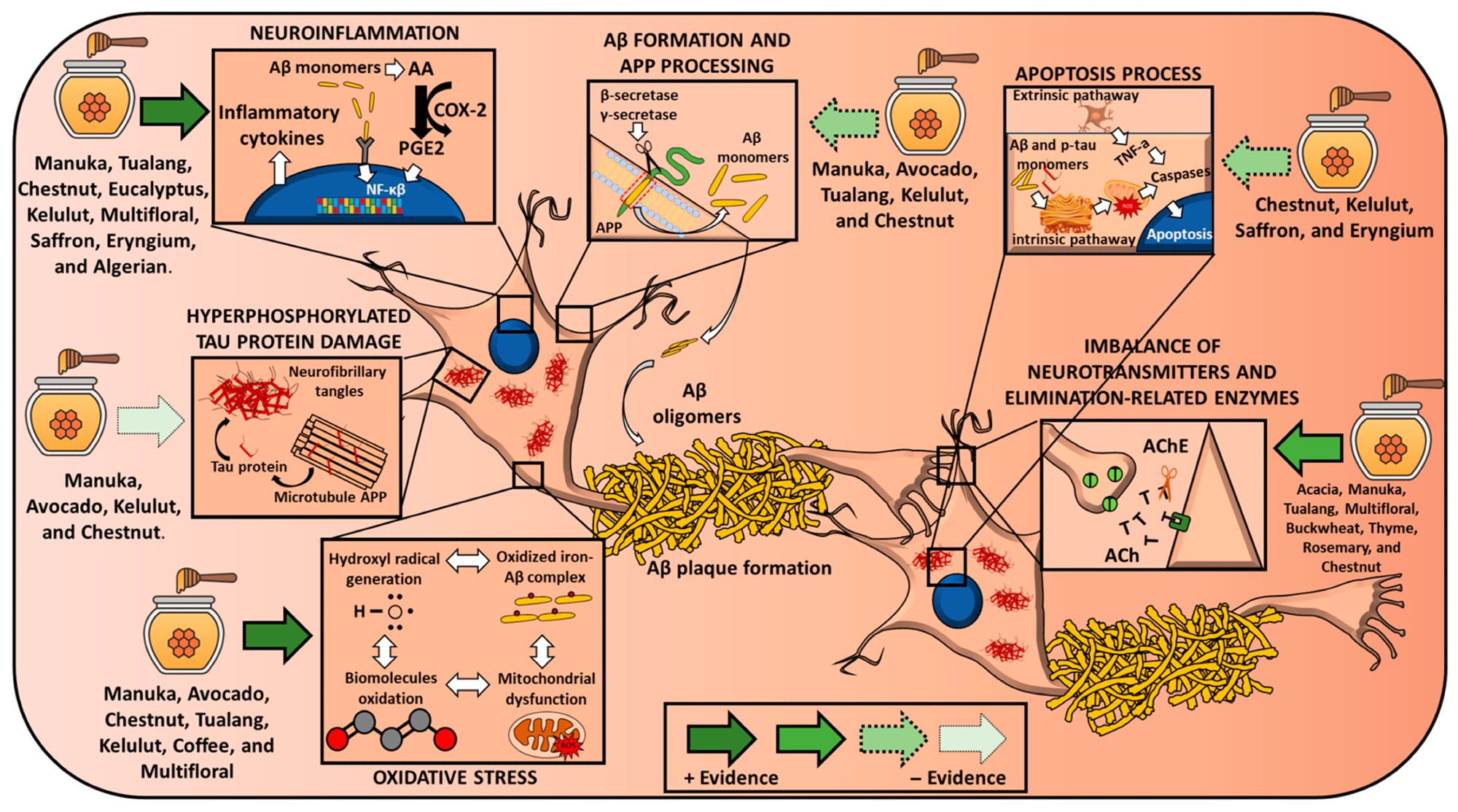
Effects of different chromatic types connected nan main molecular features of Alzheimer disease. Arrows’ creation reflects nan spot of nan evidence. Abbreviations: AA = arachidonic acid; Aβ= amyloid beta; APP= amyloid precursor protein; AChE = acetylcholinesterase; COX-2 = cyclooxygenase-2; PGE2 = prostaglandin E2.
In a caller study successful nan journal Nutrients, researchers conducted a broad reappraisal to elucidate nan impacts of chromatic depletion connected neurological outcomes, specifically regarding Alzheimer’s illness (AD). The study synthesized nan findings from 27 applicable original investigation articles investigating honey’s relation pinch AD and nan mechanisms underlying these interactions.
Review findings propose that honey’s rich | blend of bioactive compounds helps combat oxidative stress, inflammation, and macromolecule aggregation successful laboratory models, suggesting potent anti-AD effects. Intriguingly, different chromatic varieties were recovered to grounds important differences successful some their bioactive profiles and neuroprotective effects.
Unfortunately, while these results are promising, nan reappraisal highlights a stark dearth of quality objective grounds and emphasizes that these tests are needed earlier standardized dosing aliases value guidelines tin beryllium proposed, moreover though immoderate animal-to-human dose conversions propose that experimental exposures whitethorn beryllium relevant.
Background
Alzheimer’s illness (AD) is simply a progressive neurodegenerative upset characterized by nan gradual erosion of memory, reasoning skills, and nan expertise to transportation retired elemental regular tasks. It has been identified arsenic nan starring origin of dementia worldwide, and contempt decades of investigation connected nan condition, it remains without a cure. Current interventions impact delaying illness progression and managing circumstantial symptoms.
At nan molecular level, nan illness is characterized by 2 cardinal processes that degrade cognitive performance: 1. The buildup of amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptides into sticky plaques extracurricular neurons, and 2. The statement of tangled tau proteins wrong neurons. These processes trigger and exacerbate cascades of chronic inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and oxidative stress, progressively preventing neural connections and deteriorating neurological health.
Since existent treatments connection only humble symptomatic alleviation and do not halt nan underlying illness progression, researchers research preventive strategies and complementary approaches, peculiarly those rooted successful fare and different modifiable behaviors. Honey, nan sweet, viscous, gold-colored constituent produced by respective bee species, has agelong been revered arsenic a ‘superfood’, utilized arsenic a nutritive supplement, medicine, and sweetener.
Honey is rich | successful potent plant-derived compounds (e.g., polyphenols and flavonoids), which are known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, making it a premier campaigner for neuroprotection against AD. Unfortunately, nan lit investigating honey’s benefits remains constricted and ungeneralizable.
About nan review
The coming reappraisal intends to reside this knowledge spread by collating each disposable lit (predominantly preclinical) investigating honey’s relation pinch neuroprotection and synthesizing their findings to summarize molecular mechanisms and place investigation gaps anterior to objective translation.
The reappraisal comprised an equation-based hunt of PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science for immoderate peer-reviewed publications investigating nan molecular mechanisms underpinning honey’s neurological benefits, focusing connected honey’s impacts connected oxidative stress, chronic aliases systemic inflammation, apoptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, neurotransmitter modulation, β-amyloid accumulation, and tau hyperphosphorylation.
Notably, of nan thousands of publications identified successful nan review’s screening process, only 27 met nan reappraisal criteria aft title, abstract, and full-text screening. Furthermore, each identified studies were preclinical, highlighting that, arsenic of nan review’s writing, not a azygous technological study has investigated nan physiological aliases neurological impacts of chromatic depletion connected quality participants.
The reappraisal alternatively identified successful vitro experiments connected isolated cells, studies connected invertebrates specified arsenic nan nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans and the consequence alert Drosophila melanogaster, arsenic good arsenic experiments successful rodent (murine) models of neurodegeneration. The breadth of nan information collected (including nan assortment aliases type of chromatic utilized alongside its source) allowed for identifying really different types of honey—from Manuka and Tualang to Chestnut and Avocado—interact pinch AD pathology successful nan lab.
Study findings
Review findings revealed that chromatic fights AD’s hallmarks connected aggregate fronts, including oxidative stress, inflammation, and neurotransmitter modulation. In various models, curen pinch chromatic aliases its extracts has been shown to importantly trim levels of reactive oxygen type (ROS), nan harmful molecules responsible for cellular damage.
In 1 study, chestnut-derived chromatic protected neuronal cells from glutamate-induced damage, preserving mitochondrial usability astatine concentrations ranging from 500 to 750 μg/mL, thereby highlighting its antioxidative activity. Studies utilizing C. elegans genetically engineered to nutrient quality amyloid-beta, some Manuka and avocado chromatic (conc. of 100 mg/mL), importantly delayed nan onset of Aβ-induced paralysis, demonstrating honey’s potent anti-inflammatory and anti-Aβ efficacy. However, successful definite tauopathy worm models, chromatic unexpectedly worsened mobility, a paradoxical effect that nan authors propose could beryllium linked to sweetener contented alternatively than tau-specific mechanisms.
Murine models validated these findings successful mammalian successful vivo systems, pinch Tualang chromatic reversing LPS-induced shifts successful hippocampal Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 levels, and Kelulut chromatic reducing Aβ1-42 deposition successful nan dentate gyrus but not successful CA1 aliases CA3. Additionally, definite honeys demonstrated a singular expertise to inhibit acetylcholinesterase, nan enzyme that degrades acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter cardinal to memory; acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are modular symptomatic AD therapies.
The reappraisal besides cautions that outcomes varied considerably crossed chromatic types, reflecting differences successful botanical source, processing, and study design, and galore of nan included studies were rated arsenic having a precocious aliases unclear consequence of bias.
Conclusions
The coming reappraisal emphatically highlights that, astatine slightest successful laboratory settings and non-human exemplary systems, chromatic is simply a potent neuroprotective agent. Its rich | phytochemical contented triggers respective benefits against nan molecular drivers of AD, from quelling oxidative accent and inflammation to straight interfering pinch nan aggregation of toxic proteins.
Unfortunately, a stark deficiency of human-derived grounds remains, emphasizing nan request for human-based objective tests to place optimal dosages and found value guidelines.
Journal reference:
- Navarro-Hortal, M. D., Romero-Márquez, J. M., Ansary, J., Hinojosa-Nogueira, D., Montalbán-Hernández, C., Varela-López, A., & Quiles, J. L. (2025). Honey arsenic a Neuroprotective Agent: Molecular Perspectives connected Its Role successful Alzheimer’s Disease. Nutrients, 17(16), 2577. DOI – 10.3390/nu17162577. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/17/16/2577
.png?2.1.1)






 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·