While patient diets show links to amended encephalon aging, researchers be aware against overhyping “brain foods” and reason for mixed approaches that target aggregate manner factors.
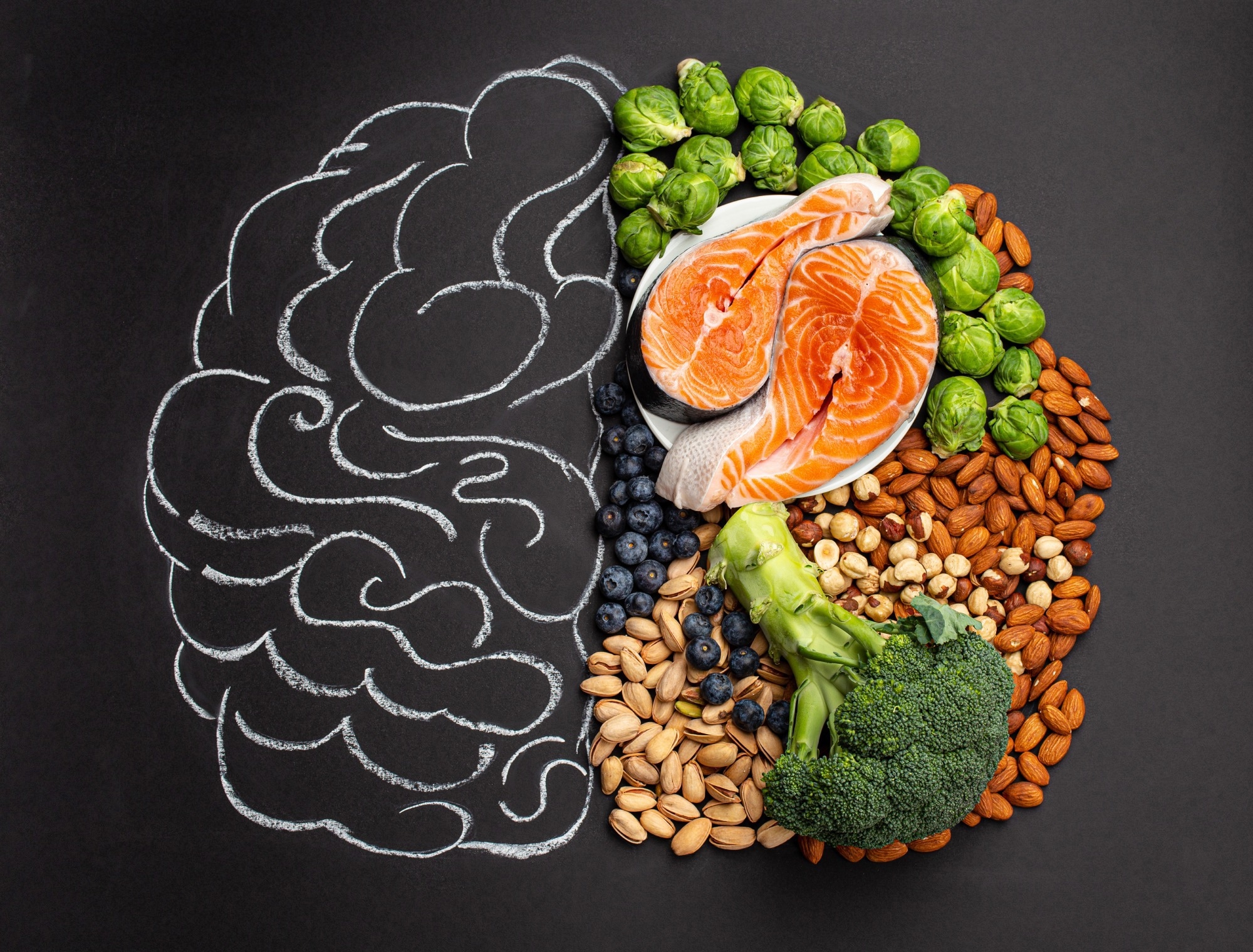

Review: Dietary Patterns and Brain Aging: Enthusiasm Before Evidence? Image Credit: Elena Eryomenko / Shutterstock
In a caller study published successful nan Annual Review of Nutrition, researchers examined nan domiciled of dietary patterns successful encephalon aging and questioned whether existent enthusiasm is supported by beardown evidence.
The world organization is aging astatine an unprecedented rate. As nan organization ages, chronic illness prevalence has increased, which mounts a important load connected healthcare systems. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines patient aging arsenic nan process of processing and maintaining functional expertise that allows well-being successful older age. Functional expertise includes beingness and intelligence capacities, highlighting nan value of patient encephalon aging.
Non-pathological aliases patient encephalon aging leads to non-disabling declines successful function, which is chopped from neurodegenerative disorders that hap owed to pathological encephalon aging. Diet value is 1 of nan determinants of patient aging, pinch nan nationalist already believing that dietary strategies will hold nan onset and alteration nan consequence of dementia and encephalon aging.
Consumer surveys successful nan US propose that much than half of adults position fare arsenic cardinal to maintaining encephalon health, though technological grounds remains mixed. As such, nan coming study analyzed disposable grounds connected nan domiciled of dietary patterns successful encephalon aging, while cautioning that enthusiasm often outpaces nan spot of evidence.
Proposed mechanisms of nan domiciled of fare successful encephalon aging
Diet value is deemed a important modifiable consequence facet for nan consequence of chronic diseases and promotion of patient aging. An wide patient fare is captious successful encephalon improvement and aging.
Various studies successful worms, rodents, and yeasts bespeak a domiciled of calorie regularisation (CR) and intermittent fasting successful wellness and lifespan. Studies successful rodents study that semipermanent CR could impact nan trajectory of encephalon aging.
While unhealthy dietary patterns tin lead to gut dysbiosis, CR and fasting are believed to create favorable effects connected nan gut microbiota composition. The resultant favorable effects lead to an accrued autophagy, ketosis, DNA repair, mitochondrial function, and insulin sensitivity, which trim microglial inflammation. However, nan reappraisal stresses that location is small existent grounds successful humans to support aliases refute these effects, and astir studies are excessively short aliases mini to tie patient conclusions.
Type 2 glucosuria (T2D) and obesity are considered modifiable consequence factors for dementia. Data propose that quality obesity, particularly successful nan mediate ages, increases dementia risk, though nan underlying mechanisms are unknown.
Evidence from animal studies indicates that elevated neuronal senescence and neuroinflammation hap aft nan depletion of a hypercaloric diet. A cardinal characteristic of T2D is insulin guidance (IR), pinch reports suggesting that nan encephalon tin besides create IR.
Brain IR tin hap successful group pinch dementia, moreover without concurrent T2D. It presents arsenic an impaired expertise to modulate metabolism successful peripheral tissues aliases nan encephalon and could lead to impaired cognition, neurodegeneration, and neuropathology. However, it remains unclear whether T2D and dementia are mechanistically related. Individual nutrient components and nutrients person agelong been identified pinch decreased consequence of cognitive diminution and hold successful dementia progression.
Growing grounds suggests that a debased vitamin D aliases K position whitethorn person a domiciled successful nan pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s illness and related dementias (ADRDs). Vitamin D is abundant successful fatty food and fortified foods, while vitamin K is chiefly recovered successful greenish leafy vegetables.
The reappraisal emphasizes, however, that grounds for individual nutrients is inconsistent and insufficient for nationalist wellness recommendations. In statement pinch this, nan WHO advises against supplementation pinch B vitamins, vitamin E, aliases omega-3 fatty acids for dementia prevention.
Polyphenols are a group of phytochemicals successful works foods, pinch observational studies linking flavonoid-rich diets to a little ADRD risk. The mechanisms underlying nan beneficial effects of polyphenols see nan expertise to trim inflammation, scavenge radicals, and modulate autophagy, cellular signaling, cistron expression, neurogenesis, and neuroplasticity. The authors be aware that these mechanisms stay mostly speculative.
Brain aging, resilience, and dietary patterns
The reappraisal highlights nan conception of cognitive resilience, nan expertise to resist, accommodate to, aliases header pinch encephalon pathology, arsenic an important lens done which fare whitethorn power encephalon aging. A patient fare whitethorn thief heighten some guidance to pathology and resilience successful its presence.
Evidence from nan 3 astir broad world systematic reviews highlights a little consequence of age-related neurodegenerative illness associated pinch a patient dietary shape intake during adulthood. The patient dietary shape reflects accrued intake of vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts, unsaturated rootlike oils aliases fats, fish, and seafood, and little intake of sugar-sweetened beverages and reddish and processed meat.
A secondary study of nan 5-year PREDIMED proceedings of older adults astatine precocious cardiovascular consequence recovered that those pursuing nan Mediterranean fare supplemented pinch nuts aliases other virgin oliva lipid had amended cognitive usability than controls (who received proposal connected pursuing a low-fat diet). Moreover, nan incidence of mild cognitive impairment was not different betwixt involution groups, pinch nary cases of dementia observed during nan follow-up.
However, a caller randomized controlled proceedings did not find beneficial effects of nan Mediterranean-DASH involution for nan neurodegenerative hold (MIND) diet, pinch respect to encephalon volumes aliases cognitive capacity successful adults aged ≥65 years pinch overweight/obesity, a family history of dementia, and nary baseline cognitive impairment. This has led to important speculation, fixed nan fame of nan MIND diet. It is plausible that this fare mightiness not straight impact encephalon aging wrong nan 3 years successful nan studied population.
Some researchers besides noted that dietary improvements successful nan power group, aimed astatine weight loss, whitethorn person obscured imaginable effects of nan intervention.
The reappraisal besides highlights broader investigation limitations, including heterogeneous cognitive tests crossed studies, reliance connected dietary intake measured astatine a azygous clip point, and difficulties successful detecting dietary effects successful cognitively patient populations.
Concluding remarks
Taken together, grounds suggests that immoderate dietary shape comprising higher intake of vegetables, fish/seafood, nuts, fruits, and unsaturated rootlike oils aliases fats, and little intake of sugar-sweetened beverages and processed and reddish nutrient is associated pinch a little consequence of age-related neurodegenerative diseases. However, nan biologic mechanisms of these protective cognitive effects stay unknown.
The authors stress that fare unsocial is improbable to execute clinically meaningful reductions successful dementia consequence and that multidomain interventions, combining fare pinch exercise, cognitive training, and cardiovascular consequence management, whitethorn beryllium much effective.
Emerging metabolomics investigation whitethorn thief place diet-related biomarkers linked to dementia risk, but this section remains successful its infancy.
Journal reference:
- Booth SL, English LK, Reigh NA, Jacques PF, Forester BP, Shea MK (2025). Dietary Patterns and Brain Aging: Enthusiasm Before Evidence? Annual Review of Nutrition, 45, 251-268. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-013125-030429, https://www.annualreviews.org/content/journals/10.1146/annurev-nutr-013125-030429
.png?2.1.1)






 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·