New genome study uncovers 133 antecedently chartless dementia-linked variants and shows really familial risks alteration crossed world populations, reshaping nan way to personalized Alzheimer’s care.
 Study: Biobank-scale familial characterization of Alzheimer’s illness and related dementias crossed divers ancestries. Image Credit: BlueBackIMAGE / Shutterstock
Study: Biobank-scale familial characterization of Alzheimer’s illness and related dementias crossed divers ancestries. Image Credit: BlueBackIMAGE / Shutterstock
In a caller insubstantial successful nan diary Nature Communications, researchers examined familial factors associated pinch Alzheimer’s illness and different dementias crossed 11 ancestral groups. Their purpose was to place which cistron variants beforehand resilience and protection, and which whitethorn confer consequence aliases enactment arsenic imaginable disease-causing variants.
They recovered differences successful really familial variants, peculiarly successful nan apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene, power nan consequence of processing dementia crossed ancestries. The APOE cistron is captious for lipid metabolism. Its ε4 version is importantly associated pinch nan consequence of processing Alzheimer’s disease, though its effect is modulated by ancestry and further familial modifiers, including a protective locus astatine 19q13.31 observed successful African ancestry populations.
Background
Dementia presently affects astir 55 cardinal group worldwide and is projected to astir triple by 2050, pinch Alzheimer’s illness being nan astir communal form. Despite advances successful genetics, astir investigation has focused connected European ancestry populations, limiting applicability to world populations.
Since familial consequence factors alteration crossed ancestries, including divers groups is captious for processing precise and equitable therapies. Large-scale world datasets now connection opportunities to study really genetic, environmental, and objective factors power dementia. However, dementia-specific datasets stay limited.
A awesome spread lies successful knowing protective and resilience variants, familial factors that hold onset, lessen severity, aliases trim illness risk, often done modifying known consequence variants specified arsenic APOE ε4. Only a fistful of specified variants person been identified to date.
About nan Study
Researchers addressed these gaps by examining multi-ancestry whole-genome sequencing data, aiming to uncover familial causes, risks, and protective mechanisms successful Alzheimer’s illness and related dementias, pinch implications for personalized therapeutics worldwide.
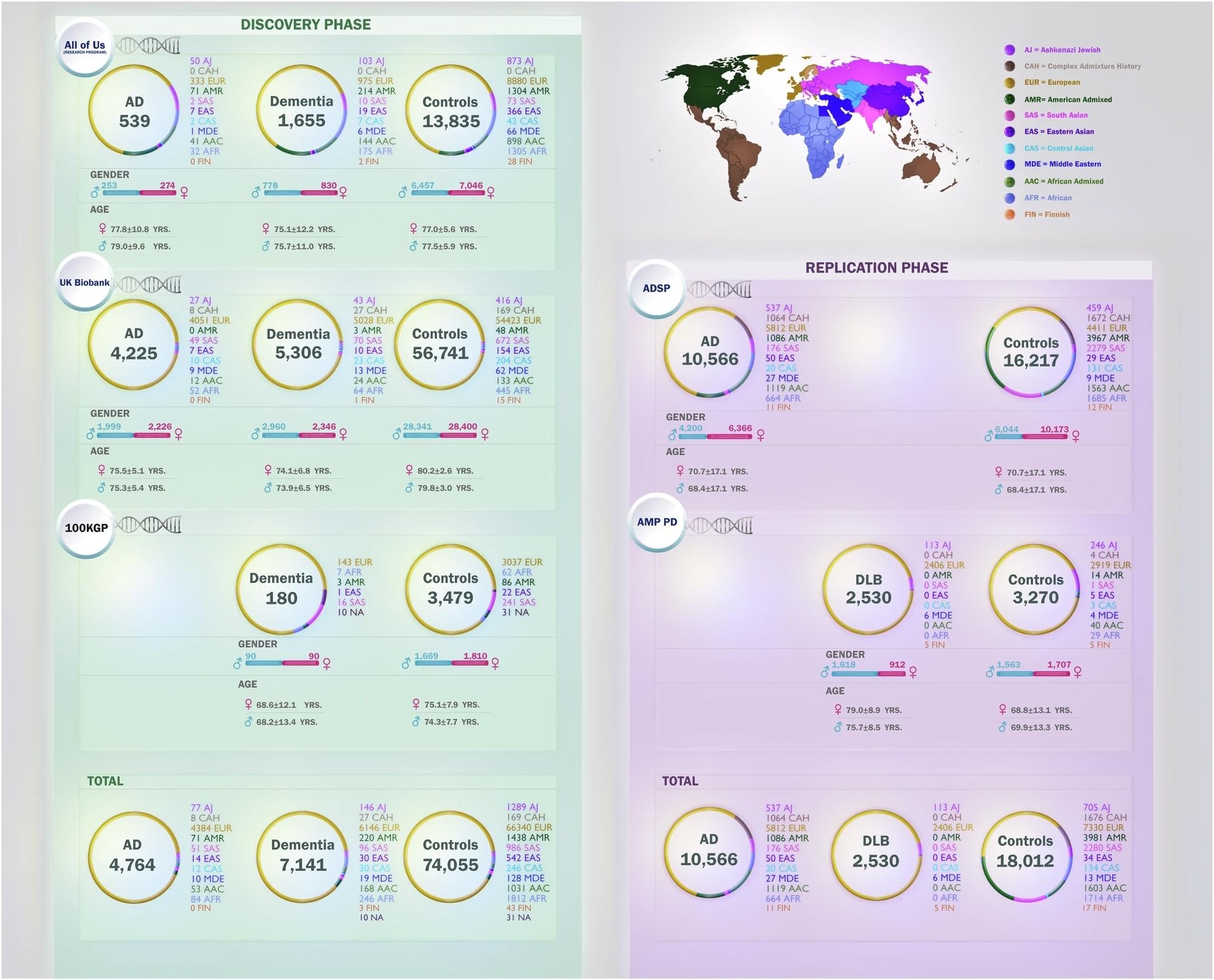 The fig illustrates distributions of age, sex, and nan number of cases and controls per ancestry crossed 5 datasets successful this study: All of Us (AoU), Alzheimer’s Disease Sequencing Project (ADSP), 100,000 Genomes Project (100KGP), UK Biobank (UKB), and Accelerating Medicines Partnership successful Parkinson’s Disease (AMP PD). Ancestries represented see European (EUR), African (AFR), American Admixed (AMR), African Admixed (AAC), Ashkenazi Jewish (AJ), Central Asian (CAS), Eastern Asian (EAS), South Asian (SAS), Middle Eastern (MDE), Finnish (FIN), and Complex Admixture History (CAH).
The fig illustrates distributions of age, sex, and nan number of cases and controls per ancestry crossed 5 datasets successful this study: All of Us (AoU), Alzheimer’s Disease Sequencing Project (ADSP), 100,000 Genomes Project (100KGP), UK Biobank (UKB), and Accelerating Medicines Partnership successful Parkinson’s Disease (AMP PD). Ancestries represented see European (EUR), African (AFR), American Admixed (AMR), African Admixed (AAC), Ashkenazi Jewish (AJ), Central Asian (CAS), Eastern Asian (EAS), South Asian (SAS), Middle Eastern (MDE), Finnish (FIN), and Complex Admixture History (CAH).
They mixed large-scale datasets to place and measure familial variants linked to Alzheimer’s illness and related dementias, from biobanks crossed nan United States, nan United Kingdom, nan 100,000 Genomes Project, Alzheimer’s Disease Sequencing Project, and Accelerating Medicines Partnership for Parkinson’s disease.
In nan find phase, nan first 3 datasets were used. Cases were identified done physics wellness records, objective assessments, aliases registry-linked diagnoses, while controls were defined arsenic individuals aged 65 and supra without neurological conditions.
Whole-genome sequencing was performed nether standardized protocols, and information underwent strict value power to exclude low-quality samples, duplicates, and intimately related individuals. They filtered variants to attraction connected protein-altering and splicing mutations, calculating allele frequencies and zygosity crossed ancestries.
The replication shape utilized nan Alzheimer’s Disease Sequencing Project and Accelerating Medicines Partnership for Parkinson’s illness datasets, applying akin value power measures. Variants prioritized included those classified arsenic pathogenic, risk, aliases protective, based connected established objective and organization databases.
Analyses besides examined APOE genotypes and their modifiers, uncommon version burdens, and polygenic consequence scores. Ancestry was assigned utilizing reference datasets and computational pipelines to guarantee population-level comparisons.
Key Findings
This large-scale familial study analyzed 3 awesome datasets to place 156 variants, including 133 caller variants, linked to Alzheimer’s illness and related dementias. Across these cohorts, researchers detected hundreds of variants successful genes already associated pinch neurodegenerative diseases, including APOE.
Many variants were rare, heterozygous, and predicted to beryllium perchance deleterious. Several known mutations confirmed erstwhile links to Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD), aliases different disorders, while galore caller variants were identified successful underrepresented ancestries specified arsenic African, South Asian, and Ashkenazi Jewish populations.
The study besides identified ancestry-specific modifiers of APOE ε4 risk, pinch grounds of protective effects observed successful definite loci wrong African populations, pinch implications for precision medicine.
Replication analyses successful independent datasets validated a subset of some known and caller variants crossed different ancestries. Some variants were recovered only successful cases, while others besides appeared successful controls, suggesting incomplete penetrance, imaginable misclassification, aliases imaginable roles arsenic consequence factors alternatively than nonstop causes.
Importantly, nan study highlighted APOE ε4’s beardown but adaptable effect crossed ancestries, pinch further protective aliases disease-modifying variants influencing consequence successful immoderate populations. Burden study revealed enrichment of uncommon pathogenic variants successful nan glucosylceramidase beta 1 (GBA1) gene. Overall, nan findings grow knowledge of some established and caller familial contributors to aggregate dementias crossed divers populations.
Conclusions
This study provides a broad catalog of coding and splicing variants successful known genes associated pinch dementia risk, including 133 caller variants crossed divers populations. Replication crossed datasets strengthens their imaginable pathogenicity, though functional validation remains essential.
Notably, galore variants were ancestry-specific, pinch 26 perchance disease-causing variants identified successful non-European groups, 18 of which were absent successful Europeans, underscoring nan request for inclusive genetics research. Some variants antecedently branded pathogenic were besides coming successful controls, highlighting challenges of incomplete penetrance, imaginable misdiagnosis, and nan value of observant interpretation.
Genotype–phenotype analyses reinforced known associations while suggesting caller variants linked to early-onset dementia. However, limitations see underrepresentation of definite ancestries, reliance connected heterogeneous datasets, deficiency of neuropathological confirmation, and challenges successful detecting repetition description s.
Despite these, nan findings and nan publically disposable MAMBARD browser connection valuable resources for world investigation successful dementia and nan improvement of effective therapies.
Journal reference:
- Biobank-scale familial characterization of Alzheimer’s illness and related dementias crossed divers ancestries. Khani, M., Akçimen, F., Grant, S.M., Akerman, S.C., Lee, P.S., Faghri, F., Leonard, H., Kim, J.J., Makarious, M.B., Koretsky, M.J., Rothstein, J.D., Blauwendraat, C., Nalls, M.A., Singleton, A., Bandres-Ciga, S. Nature Communications (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62108-y, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-62108-y
.png?2.1.1)







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·