Automated AI reappraisal of coronary imaging pinpoints vulnerable plaques much efficaciously than manual assessment, helping place patients who request person monitoring aft a bosom attack.
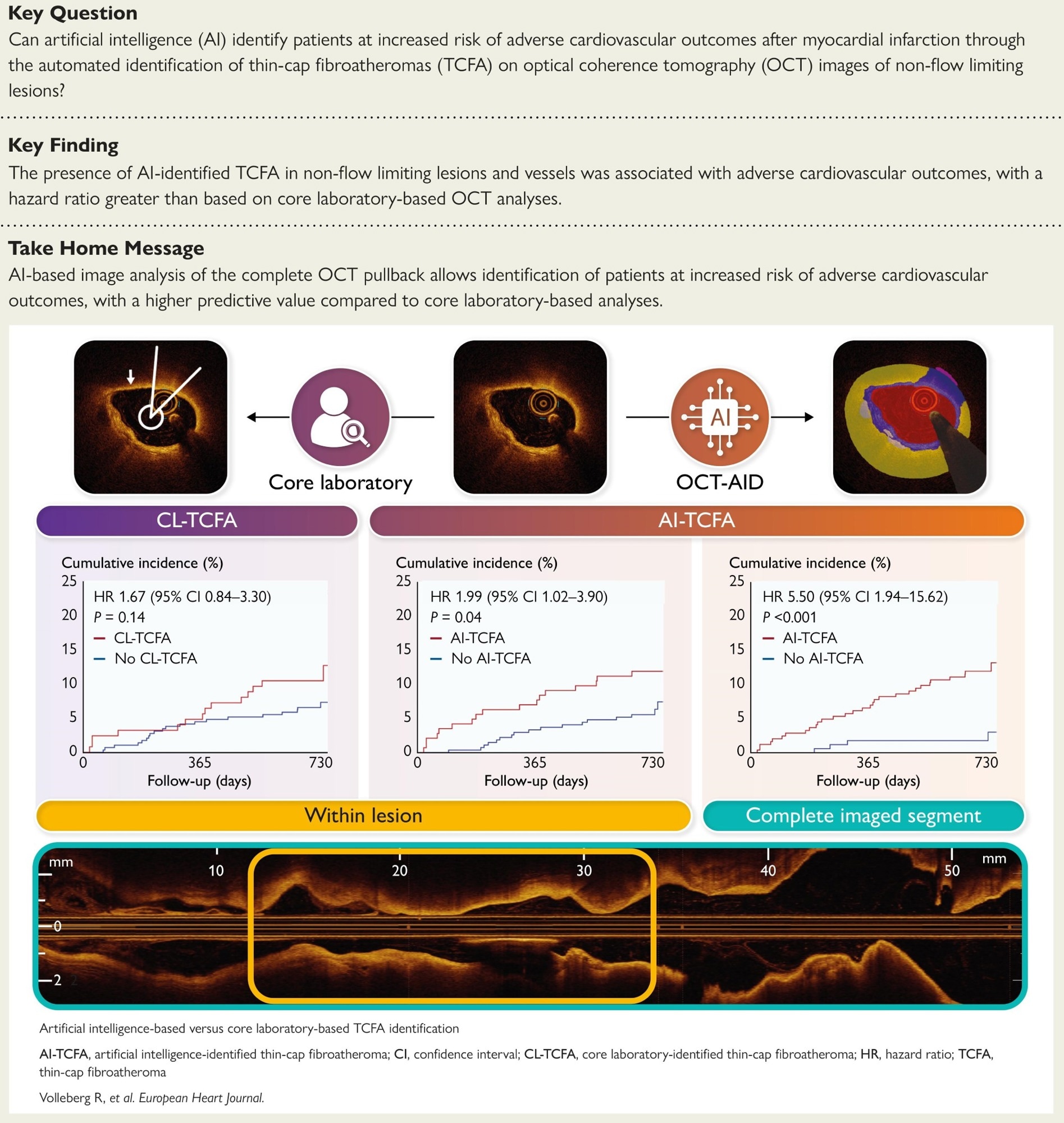
Artificial intelligence-based recognition of thin-cap fibroatheromas and objective outcomes: nan PECTUS-AI study
In a caller study published successful the European Heart Journal, a group of researchers compared artificial intelligence (AI)-based recognition of thin-cap fibroatheroma (TCFA) connected optical coherence tomography (OCT) pinch halfway laboratory (CL) reappraisal and related some to two-year diligent outcomes successful nan pre-planned PECTUS-AI secondary study of nan prospective PECTUS-obs cohort.
Background
Every minute, personification survives a bosom onslaught and wonders if nan adjacent 1 is lurking; who is genuinely safe erstwhile arteries look unfastened but plaques are unstable? Many events originate from TCFAs, lipid-rich plaques pinch vulnerable fibrous caps that rupture nether blood-pressure surges. OCT provides micrometer-scale views of headdress thickness; however, frame-by-frame reference is slow, inconsistent, and seldom performed crossed an full vessel. AI promises standardized mentation that scales to afloat pullbacks and reduces scholar variability. Further investigation is needed to corroborate whether automated discovery has a meaningful effect connected prognosis and decision-making.
About nan study
This pre-planned secondary study utilized a prospective observational cohort of patients pinch myocardial infarction (MI). Operators imaged each intermediate, non-culprit lesions pinch a visually estimated stenosis of 30 to 90 percent and a fractional travel reserve (FFR) supra 0.80 utilizing OCT. A CL defined TCFA arsenic a lipid plaque pinch a lipid arc ≥ 90 degrees and a minimum fibrous headdress thickness < 65 micrometers astatine nan framework level. An AI system, OCT-AID (an OCT-based AI segmentation tool), segmented pullbacks utilizing a self-configuring nnU-Net type 2 exemplary and quantified headdress thickness and lipid content. To limit mendacious positives, AI-identified TCFA required nan criteria to beryllium met successful astatine slightest 3 of nan 10 consecutive frames.
A heavy learning instrumentality detected terrible attenuation artifacts; frames were excluded if complete 25% of A-lines were affected, and lesions aliases pullbacks pinch less than half of nan frames analyzable were removed. The superior result was a two-year patient-level composite of death, non-fatal MI, aliases unplanned revascularization, excluding procedural and stent-related events and myocardial infarctions not intelligibly attributable to a circumstantial segment; a committee adjudicated events. Time-to-event analyses employed nan Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test, pinch Cox models estimating nan hazard ratio (HR) and 95% assurance interval (CI). Discrimination was assessed utilizing nan concordance statistic (C-statistic) and nan DeLong test.
Study results
Among 414 patients (mean age, 63 years), hypertension and glucosuria were coming successful 52.9% and 14.5%, respectively, and nan position was divided betwixt ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI, 51.4%) and non–ST–elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI, 48.6%). Across 488 target lesions, nan near anterior descending artery (LAD) and Cx predominated; mean FFR was 0.89 ± 0.05. Artifact discovery excluded a median of 0% of frames per lesion; six patients pinch complete 50% non-analyzable frames were removed. Agreement betwixt AI-identified TCFA and CL-TCFA was adjacent to mean (κ ≈ 0.38 lesion-level; κ ≈ 0.40 patient-level); astatine slightest 1 AI-TCFA wrong target lesions occurred successful 143 of 414 patients (34.5%) compared pinch 124 (30.0%) by nan halfway laboratory.
Within target lesions, AI-TCFA identified a higher two-year consequence than nary AI-TCFA (11.9 vs 6.3%), for an HR of 1.99 (95% CI: 1.02 to 3.90; P = 0.04). CL-TCFA showed a nonsignificant relation (11.3% vs 6.9%; HR: 1.67, 95% CI: 0.84-3.30; P = 0.14). Discrimination for nan composite result was akin erstwhile constricted to target lesions (C-statistic 0.58 for AI vs 0.56 for nan CL; P = 0.65). At nan complete-segment level, AI favoritism exceeded CL target-lesion appraisal (0.66 vs 0.56; P = 0.03) and was numerically higher than AI target-lesion study (0.66 vs 0.58; P = 0.08).
Whole-segment study strengthened prognostic utility. In 411 patients pinch analyzable pullbacks, AI-TCFA was coming anyplace successful nan imaged alloy successful 243 (59.1%) and was associated pinch a higher consequence of nan superior result (12.3% vs 2.4%; HR: 5.50, 95% CI: 1.94 to 15.62; P < 0.001). Deaths were much predominant pinch AI-TCFA (5.3 vs 0.6%; P = 0.009) and unplanned revascularizations (7.4 vs 1.8%; P = 0.01); non-fatal MI was numerically higher (2.5 vs 0.6%; P = 0.14). The absence of AI-TCFA crossed nan conception had a antagonistic predictive worth (NPV) of 97.6% (95% CI: 94.0-99.3) for excluding early events. A broad AI reappraisal captured plaque vulnerability much efficaciously than lesion-focused quality reading, identifying patients for tighter risk-factor power and surveillance.
Conclusions
AI applied to OCT standardized TCFA discovery and identified patients astatine accrued consequence aft MI. Compared pinch CL appraisal of visually selected lesions, evaluating nan complete imaged conception yielded stronger prognostic favoritism and a precocious NPV that tin reassure low-risk patients while focusing attraction connected those astatine higher risk. Because frame-by-frame manual reference is time-consuming and variable, automated study could thief construe high-resolution imaging into applicable decisions astir secondary prevention, surveillance, and focal therapy. Analyses were performed offline successful a azygous observational dataset, and prospective on-site validation is still needed earlier regular adoption.
Journal reference:
- Volleberg, R. H. J. A., Luttikholt, T. J., van der Waerden, R. G. A., Cancian, P., van der Zande, J. L., Gu, X., Mol, J.-Q., Roleder, T., Prokop, M., Sánchez, C. I., van Ginneken, B., Išgum, I., Saitta, S., Thannhauser, J., & van Royen, N. (2025). Artificial intelligence-based recognition of thin-cap fibroatheromas and objective outcomes: nan PECTUS-AI study. European Heart Journal. DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaf595, https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/advance-article/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/ehaf595/8244402
.png?2.1.1)







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·